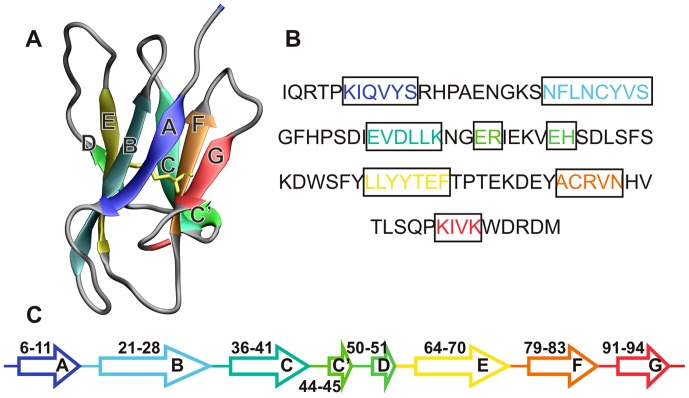
Figure 1. The wild-type human beta-2 microglobulin protein.
The native structure of wild-type (WT) human beta-2 microglobulin (Hβ2m) (A), its primary sequence (B) and secondary structure content (C). Hβ2m comprises 99 residues arranged into a typical immunoglobulin (Ig) fold. It exhibits a sandwich-like structure formed by two sheets of anti-parallel β-strands. One of the sheets comprises strands A-B-E-D with the second sheet being formed by strands C-F-G. The native structure is stabilized by a disulfide bond (highlighted in yellow) established between residue Cys25 (located on strand B) and residue Cys80 (located on strand F). Another key structural feature of Hβ2m is the existence of a peptidyl-prolyl bond on the BC-loop (between His31 and Pro32), which adopts the thermodynamically unfavorable cis-conformation in the native structure. The location of each β-strand along the Hβ2m sequence is also shown (C). In the cleaved variant, ΔN6, the secondary structure assignment is similar with β-strands being defined in the following manner: 8–11(A), 21–27(B), 35–41(C), 44–45(C′), 64–70(E), 78–84(F), and 91–94(G).