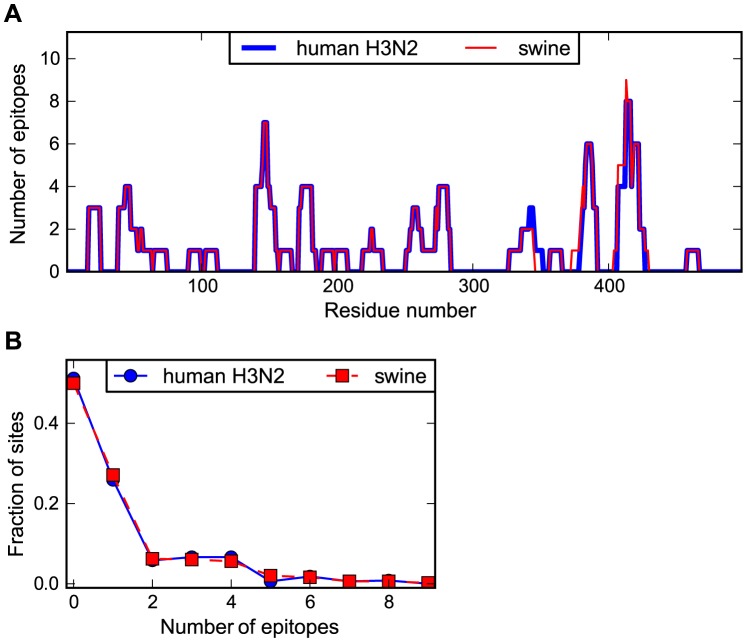
Figure 3. Human and swine NP possess similar numbers of human CTL epitopes.
(A) The number of known human CTL epitopes for each residue for human and swine NP. (B) The distribution of number of epitopes per site. The curves in (B) are consistent with the null hypothesis that the human and swine per-site epitope counts are drawn from the same underlying distribution (Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, P = 1.00). The number of epitopes for each site was determined by downloading all human MHC class I epitopes with experimentally verified T-cell responses from the Immune Epitope Database [58], and identifying epitopes between 8 and 12 residues in length that aligned with Aichi/1968 or Texas/2012 (for human NP) or with swine/Wisconsin/1957 or swine/Indiana/2012 (for swine NP) with no more than one mismatch. Redundant epitopes for the same MHC allele were removed. The epitopes per site are listed in Table S1 and Table S2. See http://jbloom.github.io/epitopefinder/example_NP_CTL_epitopes_H3N2_and_swine.html for code, input data, and detailed documentation.