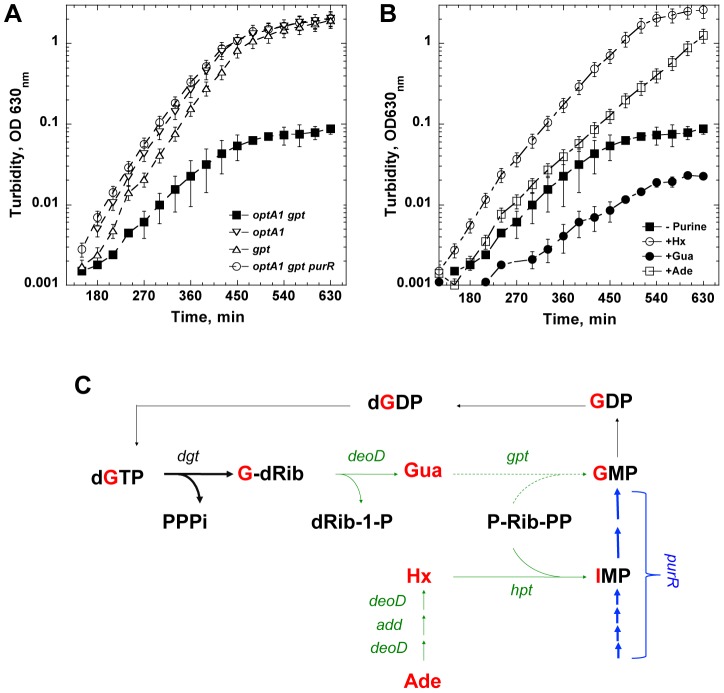
Figure 1. Defective growth upon purine starvation.
(A) Growth defect of an optA1 gpt strain upon culturing in minimal glucose medium enriched with casamino acids without added purine source. Several controls are also shown (see text for details). Error bars are from three different measurements. (B) Complementation of the growth defect of an optA1 gpt strain by hypoxanthine (Hx), adenine (Ade), but not guanine (Gua), added at 50 µg/ml each. The cultures were started from a 5,000-fold dilution of an overnight stationary culture grown in the presence of hypoxanthine. (C) Relevant metabolic pathways for de novo synthesis and salvage of guanine and guanine nucleotides, illustrating how the optA1 gpt combination may become starved for dGTP (see text for details). One alternative pathway for synthesis of GMP from Gua that is not indicated is the conversion of Gua to guanosine by the DeoD purine nucleoside phosphorylase by condensation with Rib-1-P followed by conversion of guanosine to GMP by guanosine kinase (gsk gene product). However, this pathway for GMP synthesis is not very efficient [52]. The gene symbols are: dgt - dGTP triphosphohydrolase; deoD - purine nucleoside phosphorylase; gpt - guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; hpt - hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase; add – adenosine deaminase; purR – purine repressor (transcription factor controlling de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides) [21]. Green and blue – salvage and de novo synthesis pathways, respectively. Arrows are as follows: thin – wild-type enzyme levels; thick – elevated levels of dGTP triphosphohydrolase (optA1 - dgt up-promoter) or of enzymes of the PurR regulon (purR deletion strain); dashed - lack of activities in a gpt deletion strain. Gua – guanine; Hx – hypoxanthine; Ade – adenine; dG-Rib – deoxyguanosine; IMP – inosine monophosphate; PPPi – tripolyphosphate; dRib-1P – deoxyribose-1-phosphate; P-Rib-PP – 5′-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP).