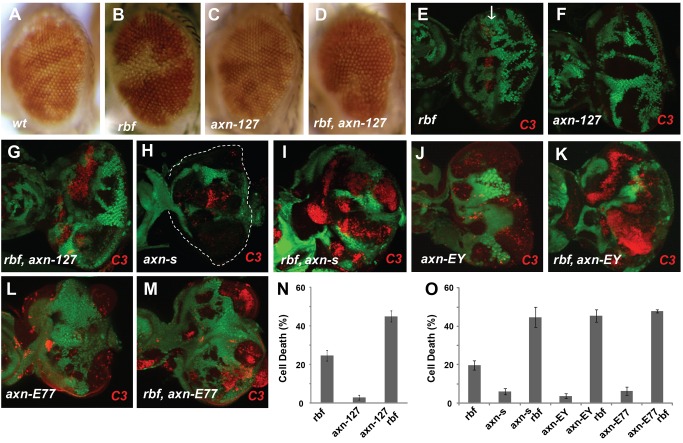
Figure 1. Synergistic cell death induced by rbf and axn mutations.
Mosaic clones for mutations of the indicated genotypes in adult eyes are marked by white color, while wild type tissues are with orange color. Comparing to wild type control clones (A), rbf mutant clones were a bit smaller (B), while axn127 mutant clones were similar to or even moderately larger (C). rbf axn127 double mutant clones were mostly eliminated in adult eyes (D). In developing eye imaginal discs, mosaic clones are marked by the absence of GFP. Activated caspase-3 (C3) staining was used to detect apoptosis (or cell death). rbf mutation induced apoptosis just anterior to morphogenetic furrow (MF) indicated by white arrow (E). axn127 mutation did not induce significant apoptosis (F), while rbf axn127 mutations induced synergistic apoptosis in a broad region anterior to MF (G). Strong axn mutant alleles, axnS044230 (axnS), axnEY10228 (axnEY), and axnE77, induced low level apoptosis (H, J, L), and induced very strong apoptosis together with rbf mutation (I, K, M). (N) Quantification of C3 levels within rbf, axn127, and rbf axn127 mutant clones anterior to the MF. (O) Quantification of C3 levels within indicated mutant clones in the whole eye discs. Error bars indicate standard deviations. Unless indicated otherwise, “synergistic apoptosis” means apoptosis induced by double mutations was significantly higher than apoptosis induced by either of the single mutant (P<0.0001).