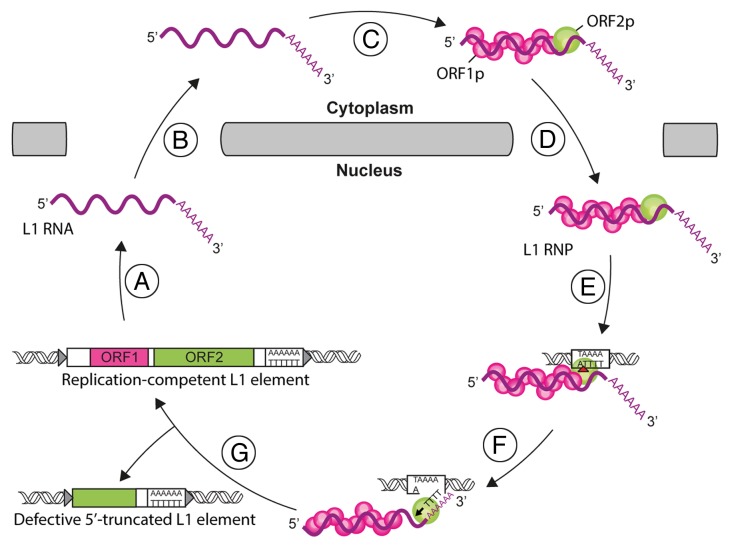
Figure 1. The L1 life-cycle. L1 replication starts by the transcription of a bicistronic mRNA (A). The L1 RNA is exported to the cytoplasm (B). ORF1p and ORF2p proteins are translated and bind to the L1 RNA to form L1 ribonucleoprotein particles (RNP) (C). The L1 RNP is imported into the nucleus (D). Integration and reverse transcription occur at the genomic target site. First, the L1 endonuclease (EN) activity nicks the target DNA (red arrowhead, E). Then, the L1 reverse transcriptase (RT) initiates the reverse transcription of L1 RNA (black arrowhead, F). The mechanisms involved in the final steps of this process and the resolution of the integration are unresolved yet (G). Partial reverse transcription can lead to 5′-truncated L1 copies.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.