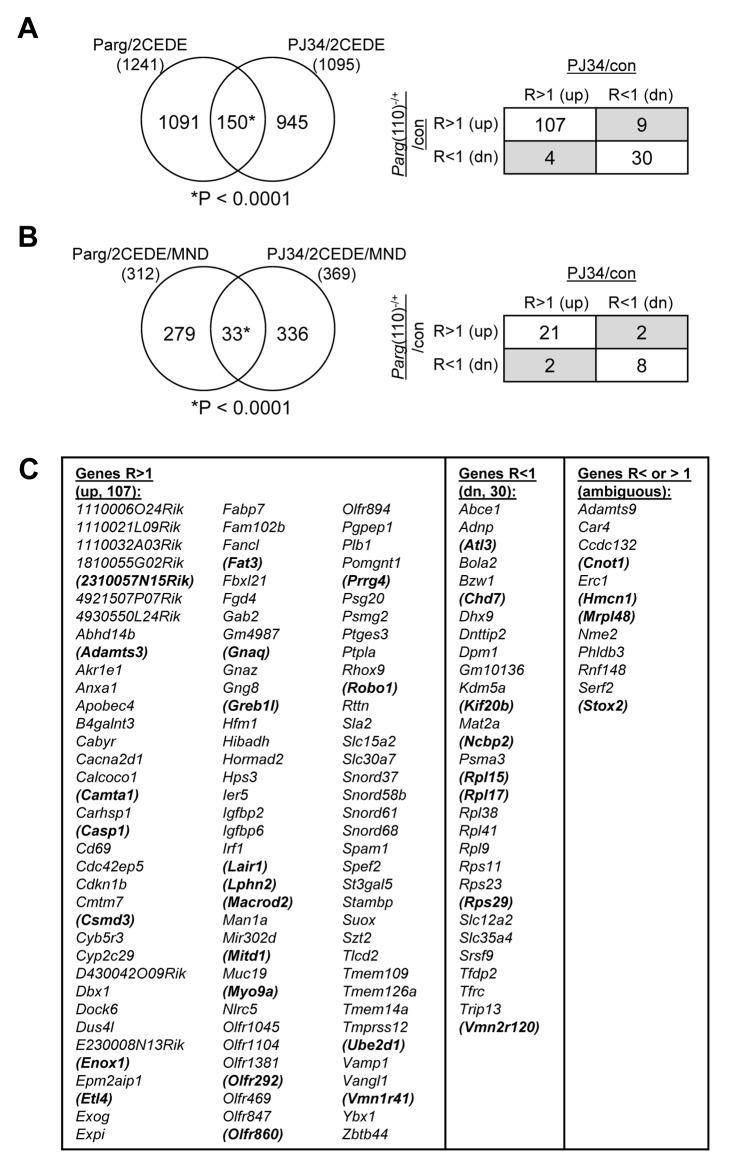
Figure 6. Shared differential gene expression in offspring from males of the two mouse models with perturbed PAR metabolism (Parg(110)−/−, PJ34 treated).
(A) The overlap of 150 differentially expressed 2-cell embryo genes (2CEDE) from Parg(110)−/− and PJ34 treated males is highly significant (Yates' and Pearson's Chi-squared tests using a genetic background of 19,472 genes, P<0.0001 in both analyses, the null hypothesis would be 70 genes in the overlap). Of the 150 genes commonly differentially expressed in embryos of the two mouse models of reduced PAR metabolism, 107 are commonly expressed at higher levels and 30 are commonly down-regulated (right panel). The shaded fields indicate genes with variable expression; these also have high coefficients of variation (Cv>5%) in the variance analyses. (B) There is also a significant overlap of 33 genes that were both differentially expressed in individual embryos and differentially histone associated in the corresponding sperm sample (2CEDE/MND genes) between the two models (Parg(110)−/− and PJ34-treated fathers (P<0.0001, the null hypothesis would have been 4.8 genes in the overlap)). The relationships of differential expression of these genes (ratio>1: R>1 or ratio<1: R<1) are again very similar for the genes in the overlap (box panel to the right). (C) Identity of the genes in the overlaps shown in (A). The 33 genes in the overlap shown in (B) are bold and in brackets. Variably (ambiguously) expressed genes are listed in column 5.