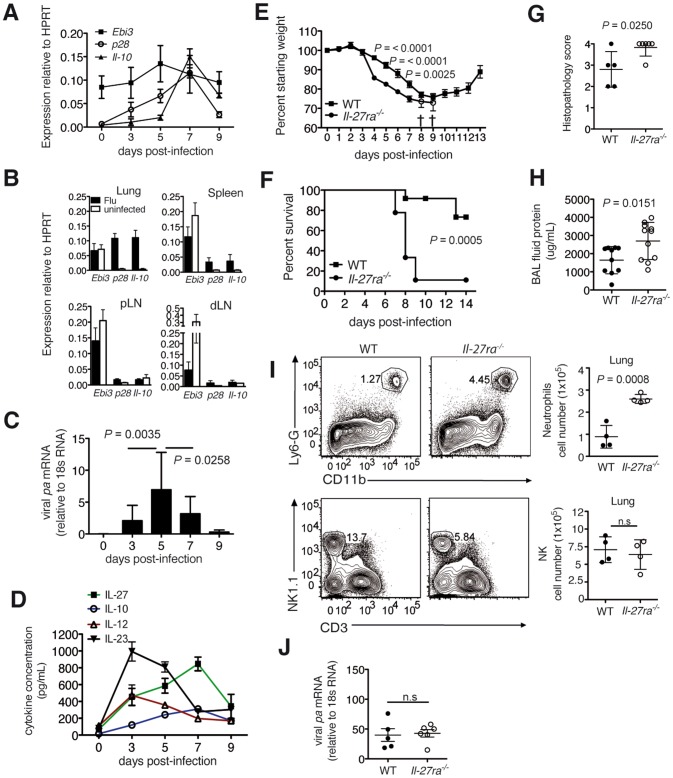
Figure 1. Absence of IL-27Rα leads to increased mortality and immunopathology during influenza.
C57BL/6 mice were infected with a sublethal dose influenza virus. Ebi3, Il-27p28 and Il-10 mRNA in the (A) lung at indicated d.p.i or (B) spleen, peripheral (pLN) and lung-draining (dLN) lymph nodes of infected or uninfected C57BL/6 mice at 7 d.p.i. (C) Influenza virus polymerase (pa) mRNA expression or (D) cytokine concentration in the lung homogenate of infected C57BL/6 mice were analyzed at indicated d.p.i. (E) Weight loss or (F) survival of infected Il-27ra−/− (n = 9) or wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 (n = 12) mice after challenge with 3000 EID influenza virus. Open circles in E represent remaining live Il-27ra−/− mice (n = 2). (G) Pathological scores of H&E-stained lungs of Il-27ra−/− mice after 7 d.p.i. with 2500 EID influenza virus (H). Protein content in the BAL fluid of Il-27ra−/− mice at 9 d.p.i. was quantified by BCA. (I) Representative FACS plots and numbers of lung-infiltrating neutrophils or NK cells of Il-27ra−/− at 8 d.p.i. (J) Viral pa mRNA in lungs of Il-27ra−/− mice at 7 d.p.i was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Lung homogenates are a 20-fold dilution of homogenized whole lung tissue. All data sets were pooled from at least two independent experiments. Values represent means ± s.d. except for E, s.e.m. P values for F were determined by log-rank survival test. P values for C, E, G, H, I and J were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. ns, not significant.