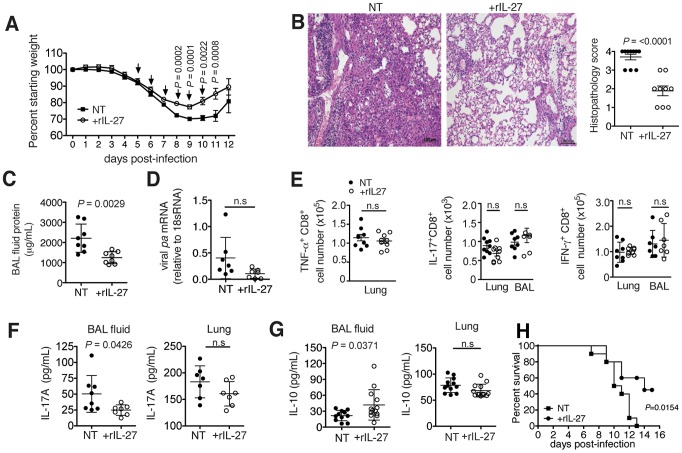
Figure 4. Late-phase treatment with rIL-27 alleviates lung immunopathology.
C57BL/6 mice were challenged with a sublethal (A to G) or lethal (H) dose of influenza virus and treated daily with rIL-27 from 5–10 (A, H) or 5–9 (B to G) d.p.i. Non-treated control mice (NT) were injected with PBS. (A) Weight loss of rIL-27-treated or NT mice. Arrows (↓) indicate points of treatment. At 9 d.p.i., (B) histological comparison of H&E-stained lungs was performed, (C) protein content in the BAL fluid was measured by BCA, (D) viral pa mRNA expression in the lungs was measured by qRT-PCR and (E) influenza virus peptide-specific cytokine production by CD8+ T cells was determined by FACS. Levels of (F) IL-17 and (G) IL-10 in the BAL fluid or lung homogenates of late-treated or NT mice at 9 d.p.i. were measured by ELISA. Lung homogenates are a 20-fold dilution of homogenized whole lung tissue. (H) Survival of mice treated with rIL27 or PBS from day 5–10 after challenge with a lethal dose of influenza virus. Values for weight loss curves are data pooled from at least two independent experiments, representing the means ± s.d. of the following numbers of mice per group: day 1–9, n = 14; day 10–11, n = 7; day 12, n = 6. Data from B to H are pooled from at least two independent experiments with similar results. P values were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. Values are means ± s.d. except for A, s.e.m.; ns, not significant. P values for H were determined by log-rank survival test (n = 10).