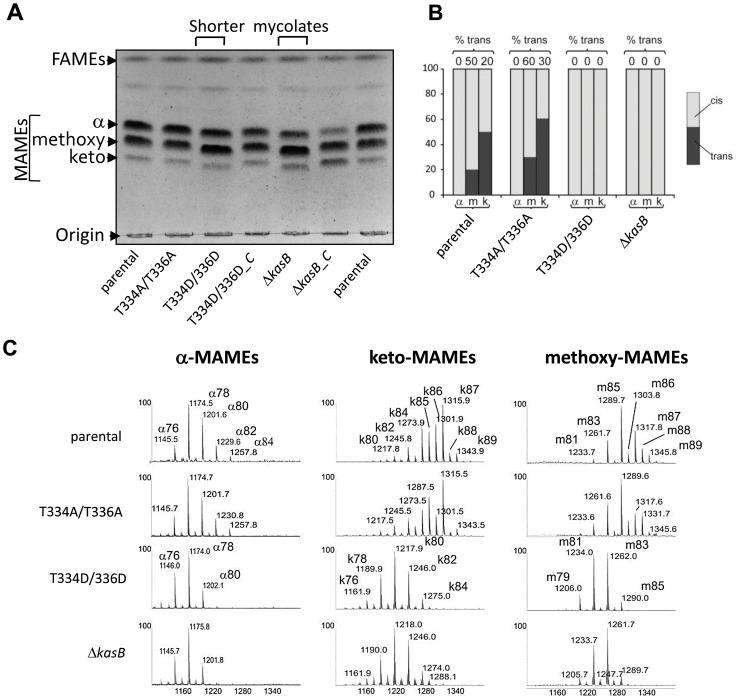
Figure 4. Structural analysis of mycolic acids in the phosphomimetic and phosphoablative kasB mutants. (A) Mycolic acid profile of the various KasB mutants and complemented strains.
Culture were grown at 37°C, harvested, and FAMEs and MAMEs were extracted and analyzed by one-dimensional TLC using hexane/ethyl acetate (19∶1, v/v; 3 runs). α-, methoxy- and keto-mycolic acids were revealed by spraying the plate with molybdophosphoric acid followed by charring. Mycolates migrating slightly faster in the Asp mutants than in the parental control strain can be observed. “-C” indicates complemented strain (with pMV261::kasB). (B) Relative proportions of cis - and trans -cyclopropanes in mycolates established from 1H NMR spectra. The relative quantification of specific signals associated to trans- and cis-cyclopropanes revealed that oxygenated mycolates synthesized by the KasB T334D/T336D and ΔkasB strains exclusively contain cis-cyclopropane rings. The % of trans-cyclopropanes for each mycolic acid sub-species and for each strain is indicated. (C) MALDI-MS analysis. Mass spectrometry analysis revealed that all three families of mycolates isolated from the KasB T334D/T336D and ΔkasB strains display reduced sizes compared to the parental or phosphoablative strains.