Fig. 4.
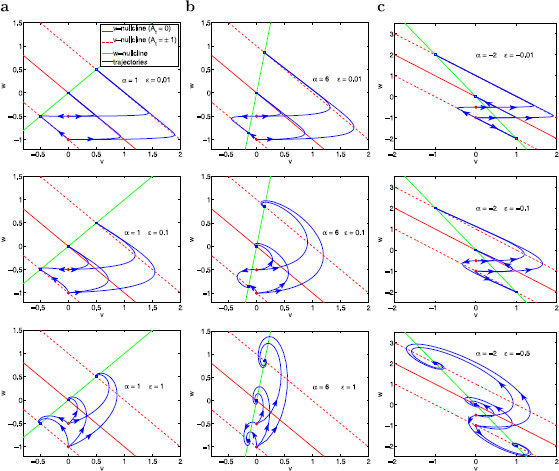
Phase-plane diagrams for the autonomous linear system (29)–(30) for various representative values of α, ϵ and . a. Top row: . Middle row: . Bottom row: . b. Top row: . Middle row: . Bottom row: . c. Top row: . Middle row: . Bottom row: . Each panel shows superimposed phase-planes diagrams for three different constant values of () generating three v-nullclines (solid-red for , dashed-red for and ) and three fixed points (blue dots on the intersections between the red and green lines). The w-nullcline (green line) is common to all values of . Solid-red line: v-nullclines for . Dashed-red lines: v-nullclines for (above) and (below). Red dots at and : representative initial conditions. Solid-blue lines: trajectories initially located at these initial points. Each trajectory emerging from the red dots corresponds to a different value of and converges to the corresponding fixed point. The fixed points in panels a-top, a-middle and b-top are stable nodes and the fixed points in panels a-bottom, b-middle and b-bottom are stable foci
