Abstract
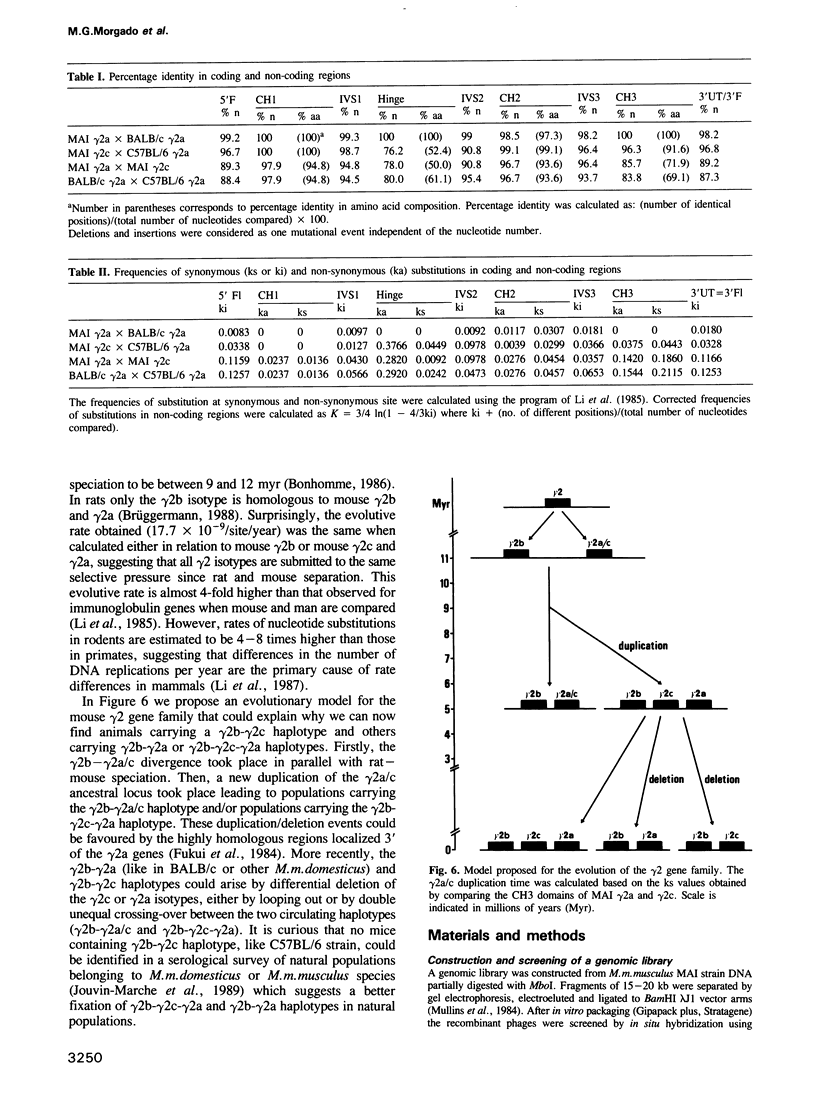
Gene conversion by the corresponding gamma 2b gene has been proposed to explain the multiple differences between the nucleic acid sequences of BALB/c (Igh-1a) and C57BL/6 (Igh-1b) gamma 2a immunoglobulin allelic genes. However, genetic analysis indicates that duplicated forms of gamma 2a genes are not only present in Eastern Asia, but also in European wild mouse populations which suggests a widespread phenomenon. In order to verify whether the gamma 2a-related isotypic genes, namely gamma 2c and gamma 2a, could correspond to those present as alleles in domestic mice (Igh-1b and Igh-1a), a genomic library from Mus m.musculus strain (MAI) was constructed. Extensive mapping of the recombinant phages and Southern blot analysis with several restriction enzymes gave the complete organization of these loci: gamma 2b (18 kb) gamma 2c (17 kb) gamma 2a (14 kb) epsilon. The homology in flanking, coding and intervening region sequences indicates that MAI gamma 2c and gamma 2a related genes correspond to C57BL/6 and BALB/c Igh-1 alleles respectively. Also, Southern blot analysis using several probes derived from exonic and intronic regions between gamma 2b and gamma 2a genes shows a 2.0- to 3.0-kb difference in the distance between gamma 2b and gamma 2a genes of BALB/c strain as compared to C57BL/6. Taken together, these results indicate that BALB/c and C57BL/6 gamma 2a genes could originate from different isotypes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonhomme F. Evolutionary relationships in the genus Mus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;127:19–34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71304-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M. Evolution of the rat immunoglobulin gamma heavy-chain gene family. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):473–482. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Hood L. Linkage and sequence homology of two human immunoglobulin gamma heavy chain constant region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1984–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K., Hamaguchi Y., Shimizu A., Nakai S., Moriwaki K., Wang C. H., Honjo T. Duplicated immunoglobulin gamma 2a genes in wild mice. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1984;1(5):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida H., Miyata T., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Honjo T., Wels J., Blattner F. Concerted evolution of the mouse immunoglobulin gamma chain genes. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2047–2053. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02090.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. M., Parsons M., Oi V. T., Huang H. J., Herzenberg L. A. Genetic characterization of mouse immunoglobulin allotypic determinants (allotopes) defined by monoclonal antibodies. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(4):311–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00372464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppi K., Jouvin-Marche E., Scott C., Potter M., Weigert M. Genetic polymorphism at the kappa chain locus in mice: comparisons of restriction enzyme hybridization fragments of variable and constant region genes. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(5):445–457. doi: 10.1007/BF00430928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaulin C., Perrin A., Abastado J. P., Dumas B., Papamatheakis J., Kourilsky P. Polymorphism in mouse and human class I H-2 and HLA genes is not the result of random independent point mutations. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(5):453–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00418091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvin-Marche E., Morgado M. G., Leguern C., Voegtle D., Bonhomme F., Cazenave P. A. The mouse Igh-1a and Igh-1b H chain constant regions are derived from two distinct isotypic genes. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(2):92–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00395856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Tanimura M., Sharp P. M. An evaluation of the molecular clock hypothesis using mammalian DNA sequences. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):330–342. doi: 10.1007/BF02603118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Wu C. I., Luo C. C. A new method for estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous rates of nucleotide substitution considering the relative likelihood of nucleotide and codon changes. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Mar;2(2):150–174. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Yasunaga T., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Obata M., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequence divergence of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 1 and gamma 2b chain genes and the hypothesis of intervening sequence-mediated domain transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2143–2147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Brody D. S., Binari R. C., Jr, Cotter S. M. Viral transduction of c-myc gene in naturally occurring feline leukaemias. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):856–858. doi: 10.1038/308856a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollo R., Auffray C., Morchamps C., Rougeon F. Comparison of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 2a and gamma 2b chain genes suggests that exons can be exchanged between genes in a multigenic family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2442–2446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollo R., Rougeon F. Gene conversion and polymorphism: generation of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 2a chain alleles by differential gene conversion by gamma 2b chain gene. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90471-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackwitz H. R., Zehetner G., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Rapid restriction mapping of DNA cloned in lambda phage vectors. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Bothwell A. L., Mueller-Hill B., Baltimore D. Multiple differences between the nucleic acid sequences of the IgG2aa and IgG2ab alleles of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Quester S., Bothwell A. Allotypic differences in murine mu genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2381–2389. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Hamaguchi Y., Yaoita Y., Moriwaki K., Kondo K., Honjo T. Japanese wild mouse, Mus musculus molossinus, has duplicated immunoglobulin gamma 2a genes. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):82–84. doi: 10.1038/298082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Takahashi N., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Nishida Y., Kataoka T., Honjo T. Ordering of mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain genes by molecular cloning. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):149–153. doi: 10.1038/289149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Takahashi N., Yaoita Y., Honjo T. Organization of the constant-region gene family of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Nakauchi H., Honjo T., Okumura K. Mouse immunoglobulin allotypes: multiple differences between the nucleic acid sequences of the IgEa and IgEb alleles. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(4):288–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00376124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. C. Statistical methods of DNA sequence analysis: detection of intragenic recombination or gene conversion. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):539–556. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe K. H., Sharp P. M., Li W. H. Mutation rates differ among regions of the mammalian genome. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):283–285. doi: 10.1038/337283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Kataoka T., Takahashi N., Obata M., Honjo T. Complete nucleotide sequence of immunoglobulin gamma2b chain gene cloned from newborn nouse DNA. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):786–789. doi: 10.1038/283786a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Miyata T., Honjo T. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobin gamma 2a gene and evolution of heavy chain genes: further evidence for intervening sequence-mediated domain transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1365–1381. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





