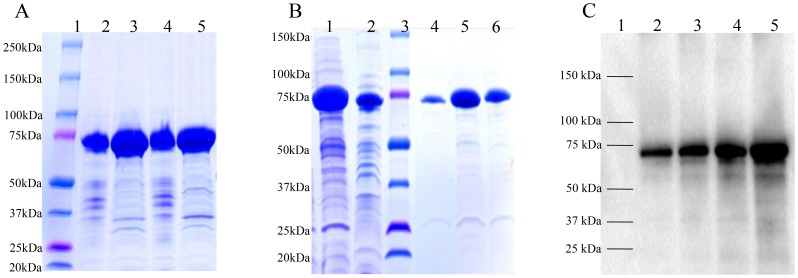
Figure 3. SDS-PAGE and Western blot analyses of mRANKL fusion proteins.
A: Comassie blue stained SDS gel showing lysates from two SHuffle E. coli-pOmR-c5X colonies expressing the mRANKL fusion proteins (∼75 kDa). Lane 1: Protein standards, molecular masses are indicated in kilodaltons (kDa); Lanes 2 and 3: Insoluble and soluble fractions from clone 1, respectively; Lanes 4 and 5: Insoluble and soluble fractions from clone 2, respectively. B: Comassie blue stained SDS gel showing purification of mRANKL using amylose resin. Lane 1: crude fusion mRANKL; Lane 2: Flow through; Lane 3: Protein standards, molecular masses are indicated in kilodaltons (kDa); Lanes 4–6: Elution fractions. C: Western blot analysis of mRANKL. Different amounts of purified fusion mRANKL was run in 4–20% SDS gel and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. Detection was performed with anti-RANKL primary antibody, goat IgG HRP-conjugated secondary antibody and chemiluminescent substrate. Lane 1: Protein marker; Lanes 2–5: 30, 50, 100, and 200 ng of purified fusion mRANKL protein respectively.