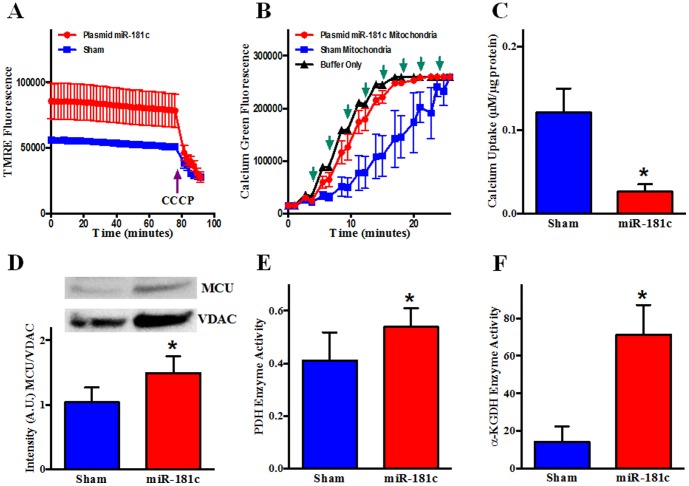
Figure 7. Effect of miR-181c on Mitochondrial Function.
Heart-derived mitochondria were isolated from the two groups of rats after 3 weeks of treatment. (A) TMRE (tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester) fluorescence was measured from mitochondria supplied with glutamate/malate from two different treatment groups for 25 min, followed by the addition of the uncoupler, CCCP (Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone). The miR-181c treatment group showed a higher level of TMRE intensity before the CCCP addition. n = 3. (B) Isolated mitochondria were incubated with Calcium Green 5N and fluorescence intensity was monitored after adding Ca2+. Following a Ca2+ pulse, fluorescence increases initially, but reverts back towards baseline as mitochondria take up Ca2+. When mitochondria take up enough Ca2+, the mPTP opens. This results in Ca2+ release and a decrease in fluorescence. (↑) indicates addition of 10 µM Ca2+. n = 3. (C) Western blot shows that miR-181c overexpression significantly increases the protein content of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) both from total heart homogenate and mitochondrial fraction. VDAC was used as a loading control. The data were normalized to the sham group. *p<0.05 vs. sham (n = 4). (D) pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) and (E) α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (αKGDH) activities were significantly higher in the isolated mitochondria from the miR-181c treated hearts compared to sham, suggesting that the mitochondrial matrix Ca2+ concentration is increased in the miR-181c treated animals.