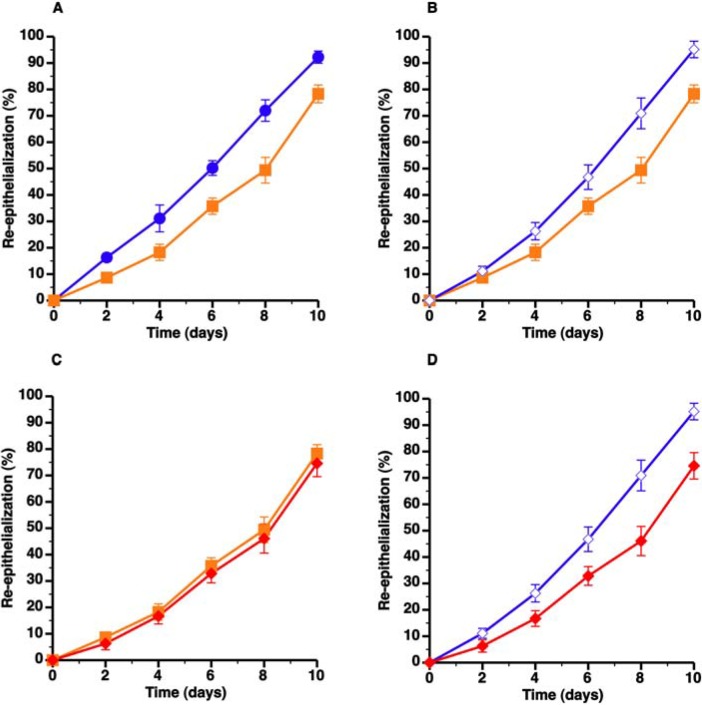
Figure 3.
Topical HDL therapy corrects delayed wound healing in C57BL/6 apoE−/− mice. The different panels illustrate the time course of wound coverage by newly formed epithelium expressed as percentage of the original wound surface. Wounds were evaluated every two days from surgical creation of the wound until 10 days later. Panel A illustrates delayed re-epithelialization in C57BL/6 apo E−/− mice ( ) compared to C57BL/6 mice (
) compared to C57BL/6 mice ( ) whereas panel B shows that topical HDL therapy (
) whereas panel B shows that topical HDL therapy ( ) corrects delayed wound healing. Panel C represents a comparison of wound coverage by newly formed epithelium in C57BL/6 apo E−/− control mice (
) corrects delayed wound healing. Panel C represents a comparison of wound coverage by newly formed epithelium in C57BL/6 apo E−/− control mice ( ) and C57BL/6 apo E−/− mice treated with control pluronic gel (
) and C57BL/6 apo E−/− mice treated with control pluronic gel ( ). The effect of control Pluronic gel (
). The effect of control Pluronic gel ( ) and HDL Pluronic gel (
) and HDL Pluronic gel ( ) is directly compared in panel D. All data represent means ± SEM.
) is directly compared in panel D. All data represent means ± SEM.