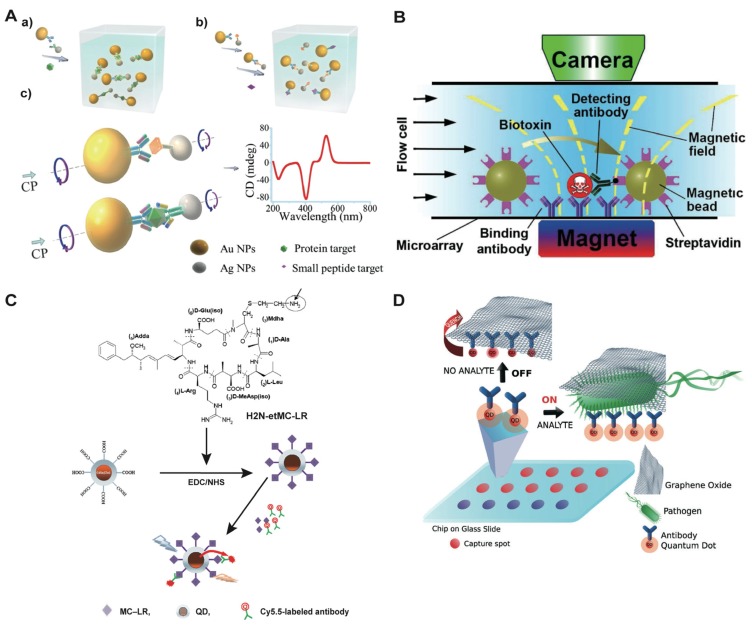
Figure 3.
(A) Schemes of gold and silver hetero dimer-based chiroplasmonic methods for (a) assaying proteins; (b) microcystin-LR. Reprinted with permission from [39]. Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society; (B) Scheme of streptavidin functionalized magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) for the simultaneous detection of five bacterial toxins in a microarray. Reprinted with permission from [24]. Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society; (C) Scheme of indirect competitive immunoassay for the detection of microcystin-LR based on the conjugation of quantum dots (QDs) and aminoethyl microcystin-LR. Reprinted with permission from [44]. Copyright 2014 Elsevier; (D) Scheme of Ab-QD-based microarrays for pathogen detection. In the presence of captured pathogen by the Ab-QD probes, the fluorescence of QDs are in the ON state, whereas in the absence ofthe pathogen, QDs are quenched by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) interaction between QDs and graphene oxide (GO) (OFF state). Reprinted with permission from [45]. Copyright 2013 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. CP: chiroplasmon; NPs: nanoparticles; EDC: 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimid; NHS: N-hydroxysuccinimide; and CD: circular dichroism.