Figure 4.
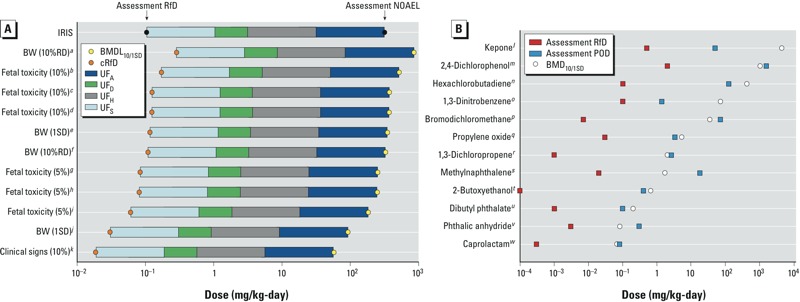
Array of batch-calculated BMDLs for the critical effects observed in studies of nitroguanidine compared with the IRIS NOAEL and RfD (A), and array of batch-calculated BMDs for selected chemicals compared with RfDs and PODs reported in human health assessments (B). Yellow circles indicate batch-calculated BMDs and BMDLs; orange circles indicate RfDs based on batch-calculated BMDLs. Uncertainty factors: UFA, interspecies uncertainty; UFD, database incompleteness; UFH, intraspecies variability; UFS, subchronic to chronic extrapolation. aReduced body weight gain. bRetarded ossification of pubis. c< 3 sternebrae ossified. d< 3 caudal vertebra ossified. eReduced weight gain in female rats. fReduced weight gain in female rats. gRetarded ossification of pubis. h< 3 caudal vertebra ossified. i< 3 sternebrae ossified. jReduced body weight gain. kMaternal toxicity. lRenal lesions (glomerulosclerosis). mDecreased delayed hypersensitivity response. nRenal tubule regeneration. oIncreased splenic weight. pRenal cytomegaly. qNest-like infolds of the nasal respiratory epithelium. rChronic irritation. sLung adenoma or carcinoma (combined). tHemosiderin deposition in the liver. uIncreased mortality. vLung and kidney histopathology. wReduced offspring body weight.
