Figure 4.
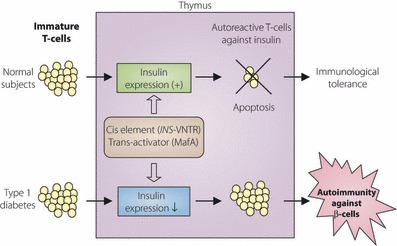
Expression of insulin in thymus and negative selection of autoreactive T‐cells against insulin. In subjects whose expression level of insulin is normal in the thymus, apoptosis is induced in insulin‐specific T‐cells upon recognition of insulin in the thymus, leading to negative selection of autoreactive T‐cells and induction of central tolerance to insulin. In subjects with reduced expression of insulin in the thymus, negative selection of insulin‐specific T cells is impaired, resulting in autoimmune attack against insulin‐producing beta‐cells of the pancreas and development of type 1 diabetes. Intra‐thymic expression of insulin is regulated by cis‐regulatory elements, such as INS‐VNTR, and trans‐acting factors, such as MafA. Functional variants in these elements or factors thus cause autoimmunity against pancreatic beta‐cells through impaired negative selection of insulin‐specific T‐cells.
