Figure 1.
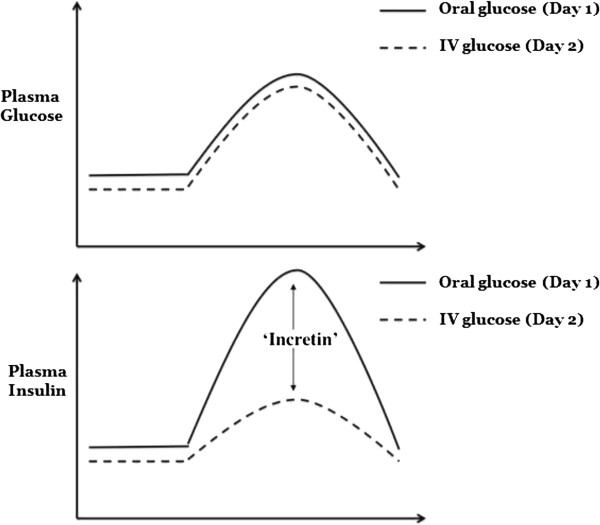
The incretin effect. There is a much greater release of insulin in response to oral glucose administration as compared with administering the same amount of glucose by intravenous (IV) infusion. Subjects were given oral glucose on day 1 with plasma insulin levels recorded. The same volunteers returned on a second day and an IV glucose infusion was titrated to match the plasma glucose excursion achieved with the oral load. The difference in the measured plasma insulin is the incretin effect, mediated by the hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide. Adapted from [17].
