Figure 7.
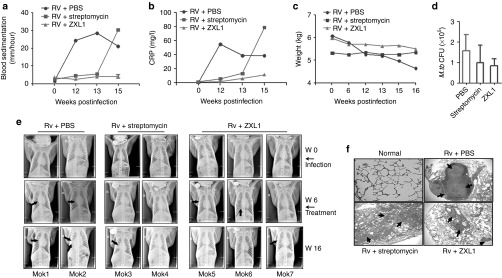
ZXL1 prevented Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tb) H37Rv infection in rhesus monkeys. A total of seven rhesus monkeys were intratracheally infected with 100 colony-forming units (CFUs) of M. tb H37Rv at week 0. At week 6, infected monkeys were randomly divided into three groups as follows: two monkeys in the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) group, two monkeys in the streptomycin group, and three monkeys in the ZXL1 group. For the ZXL1 group, monkeys were i.v. injected with ZXL1 (20 µmol/l or 100 µl/kg per monkey) three times per week for 4 weeks. For the streptomycin group, monkeys were i.m. injected with streptomycin (20 mg/kg per day) for 30 days. (a) Blood sedimentation determination. (b) C-reactive protein (CRP) determination. (c) Body weights of infected monkeys. (d) M. tb CFU assay. (e) Chest X-ray detection. The arrows indicate the pulmonary lesions. (f) Histopathology. Lung tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and evaluated by light microscopy (100×). PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.
