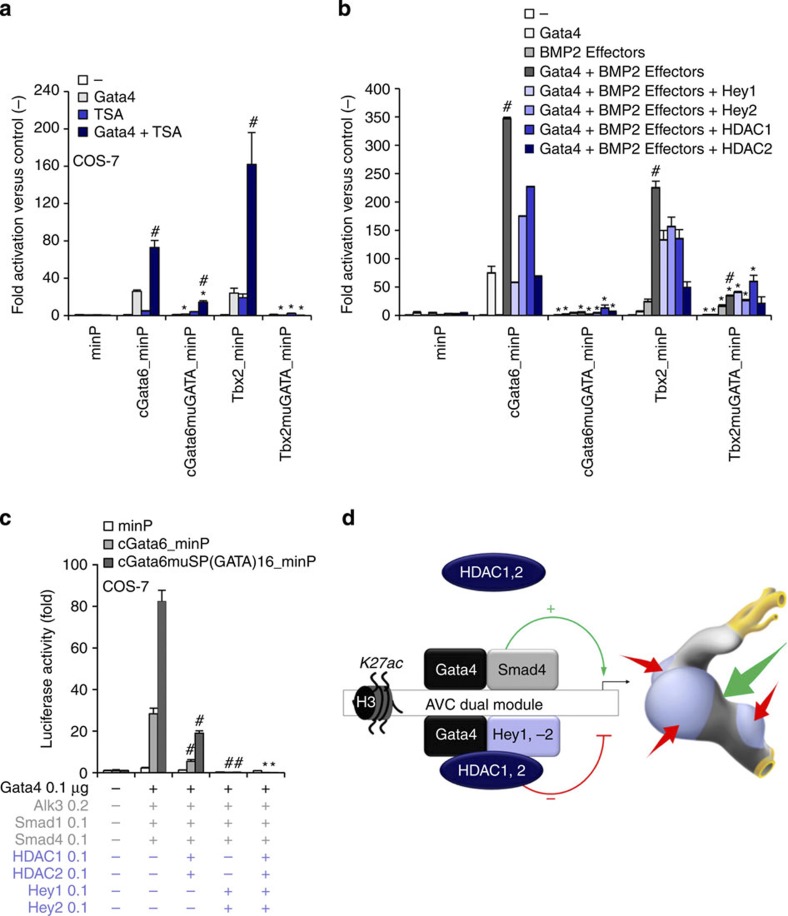
Figure 5. GATA sites serve as a scaffold to recruit functionally distinct complexes.
(a,b) In vitro reporter assays with the cGata6 (102 bp) and Tbx2 (380 bp) luciferase constructs containing mutations for GATA sites (cGata6muGATA, Tbx2muGATA). Cos-7 cells co-transfected with Gata4, Alk3CA, Smad1 and 4, Hey1, 2, HDAC1 and 2 expressing vectors or not were treated in the absence or presence of 30 nmol l−1 TSA (mean±s.e.m., n=3, #P<0.05 for Gata4 or TSA/BMP2 treatment versus Gata, TSA or BMP2 alone, *P<0.05 for mutated versus wild-type enhancers using two- and three-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)). (c) In vitro reporter assays on 102 bp cGata6 and mutated 47 bp cGata6 enhancer (cGata6muSP). Cos-7 cells were co-transfected with Gata4 and Gata4 co-activators and co-repressors (mean±s.e.m.; n=3; #P<0.05 for HDAC1, 2 or Hey1, 2 versus Gata4 and BMP2 effectors; *P<0.05 for HDAC1, 2 and Hey1, 2 versus HDAC1, 2. $P<0.05 for HDAC1, 2 and Hey1, 2 versus Hey1, 2 using three-way ANOVA. (d) GATA-binding site-enhancers recruit a Gata4/Smad4/Hat transcriptional activation complex in the AV canal and a Gata4/Hey1,2/Hdac transcriptional repression complex in the chambers, which coordinately establish AV canal gene specificity.