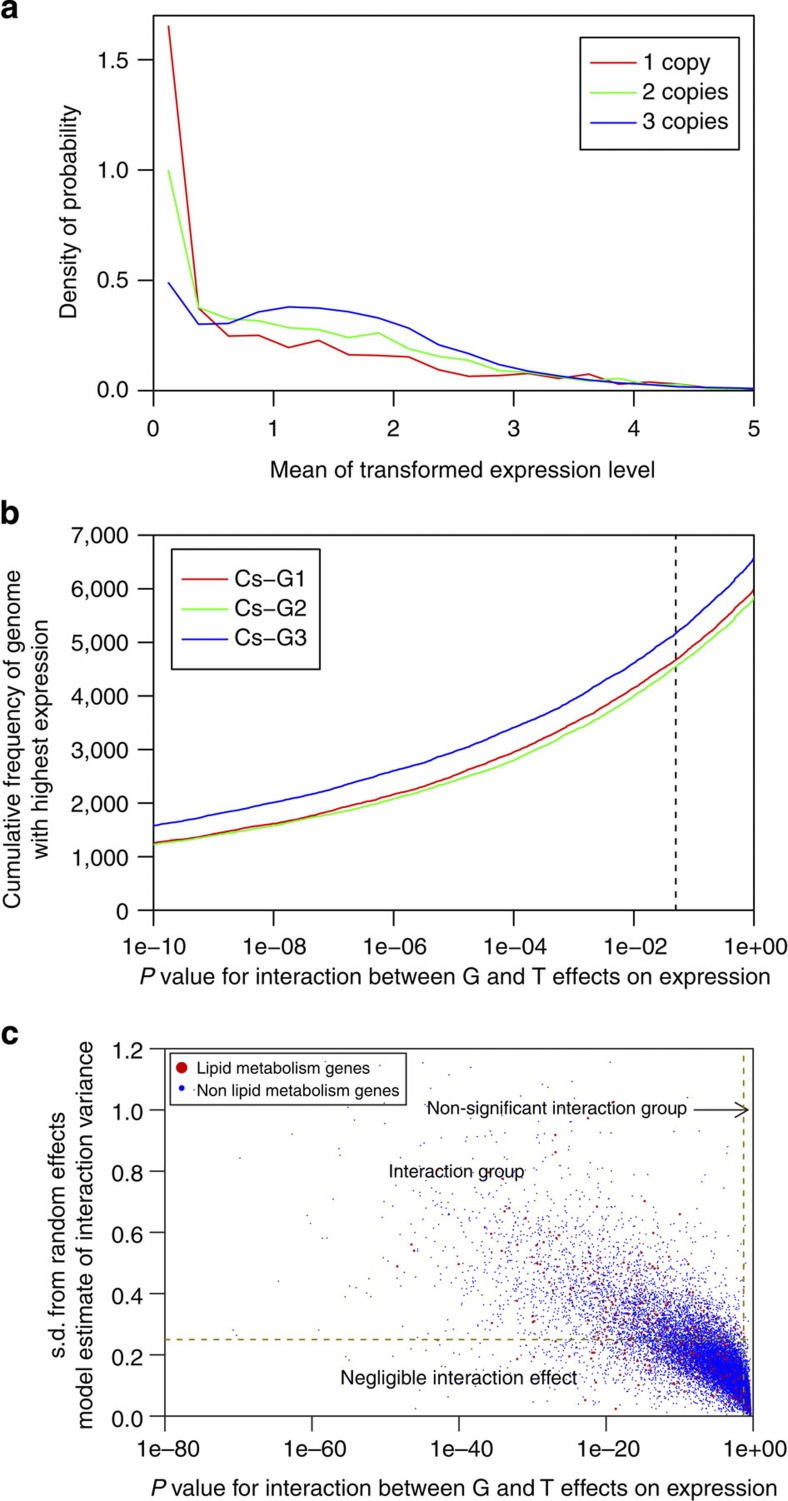
Figure 6. Gene expression dynamics reveal genome dominance and functional diversification of C. sativa homeologous genes.
(a) Relationship between gene retention rate following whole-genome triplication and the gene expression levels. (b) Cumulative frequency of homeologous genes belonging to the three sub-genomes within C. sativa with highest expression across all tissue types. P values (ANOVA test for interaction, N=108 per gene triplet) were calculated for interaction between sub-genomes (G) and tissue-type (T) effects on expression. To highlight differences between sub-genomes only the subset of the data with P>10−10 is shown. (c) Scatterplot showing the magnitude of interaction effect calculated as the s.d. from a random effects model estimate for G × T interaction variance. Homeologous triplets were classified into groups, no interaction (P>0.05; ANOVA test for interaction, N=108), negligible interaction (P<0.05 and STDEV(G × T)<0.25) and interaction (P<0.05 and STDEV(G × T)>0.25).