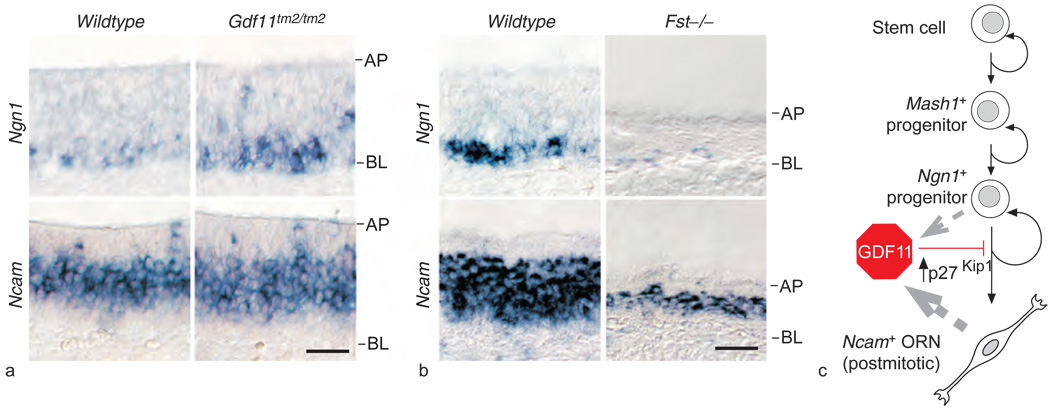
Figure 6.
Disruption of neurogenesis in mice with loss or gain of function of Gdf11. (a) In situ hybridization on horizontal sections (AP, apical layer; BL, basal layer) of olfactory epithelium of Gdf11tm2/tm2 mice reveals an increase in Ngn1-expressing cells and a corresponding increase in Ncam-expressing cells: the Ncam-expressing cell layer is thicker by 20% (9 µm), about the diameter of one olfactory receptor neuron (ORN), in Gdf11tm2/tm2 olfactory epithelium, compared to in wild type. (b) Mice lacking a functional follistatin (Fst) gene show decreased olfactory epithelium neurogenesis. In situ hybridization for Ngn1 and Ncam shows large decreases in expression of both markers as well as aberrantly thin olfactory epithelium in the Fst mutant. (c) Schematic model of growth and differentiation factor 11 (GDF11) action in ORN neurogenesis. GDF11 is produced by both Ngn1+ progenitors and Ncam+ ORNs (gray broken-line arrows). GDF11 reversibly arrests Ngn1+ progenitors through induction of the cycle-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1, thus preventing ORN generation. Reproduced from Wu HH, Ivkovic S, Murray RC, et al. (2003) Autoregulation of neurogenesis by GDF11. Neuron 37: 197–207, with permission from Elsevier.