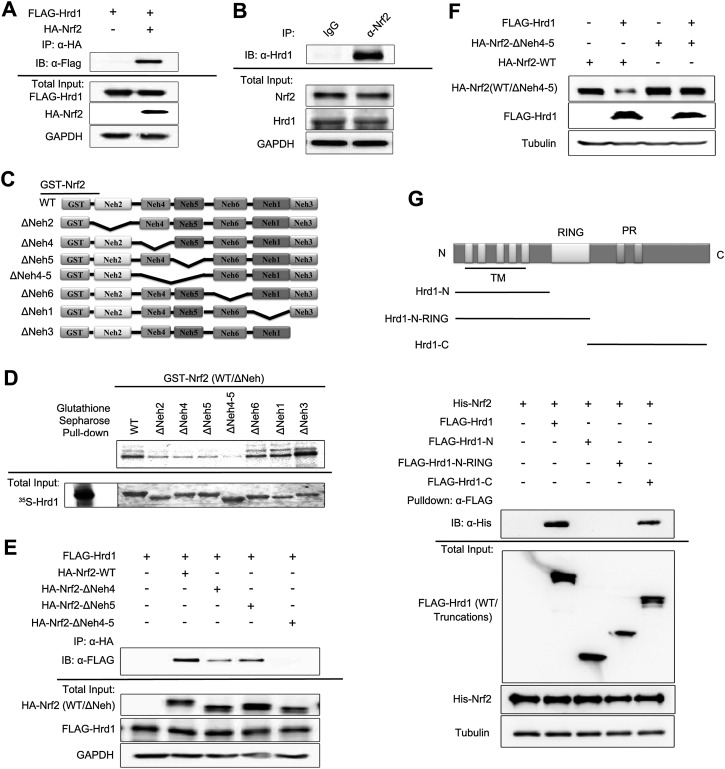
Figure 5.
Hrd1 and Nrf2 interact directly. (A) Immunoprecipitation analysis was performed using cell lysates from HEK293T cells cotransfected with Flag-Hrd1 and hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged Nrf2 (HA-Nrf2). (B) Immunoprecipitation analysis was performed using cell lysates from HEK293T cells, immunoprecipitated by normal rabbit IgG or anti-Nrf2 antibody. (C) Schematic illustration of glutathione S-transferase (GST)-tagged Nrf2-WT and its deletion mutants used for interaction domain mapping. (D) Sepharose affinity chromatography analysis of the interaction between Nrf2 and Hrd1. [35S]-Hrd1-WT was generated by in vitro transcription and translation. GST-tagged Nrf2-WT and its indicated deletion mutants were expressed and purified from Escherichia coli cells. Equal amounts of Nrf2 proteins were used for each pull-down assay. (E) Immunoprecipitation analysis was performed using cell lysates of HEK293T cells cotransfected with Flag-Hrd1 and either HA-Nrf2, HA-Nrf2-ΔNeh4, HA-Nrf2-ΔNeh5, or HA-Nrf2-ΔNeh4-5. (F) Immunoblot analysis was performed with cell lysates from HEK293T cells cotransfected with Flag-Hrd1 and either Nrf2-WT or Nrf2-ΔNeh4-5 for 24 h. (G) Immunoprecipitation of Nrf2 by Flag-Hrd1 and its mutants. HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-Hrd1 and the indicated truncation mutants. Hrd1 proteins were first immunoprecipitated using Flag-M2 beads and then incubated with His-tagged Nrf2 that was expressed and purified from E. coli cells. Equal amounts of Hrd1 proteins were used for each experiment.