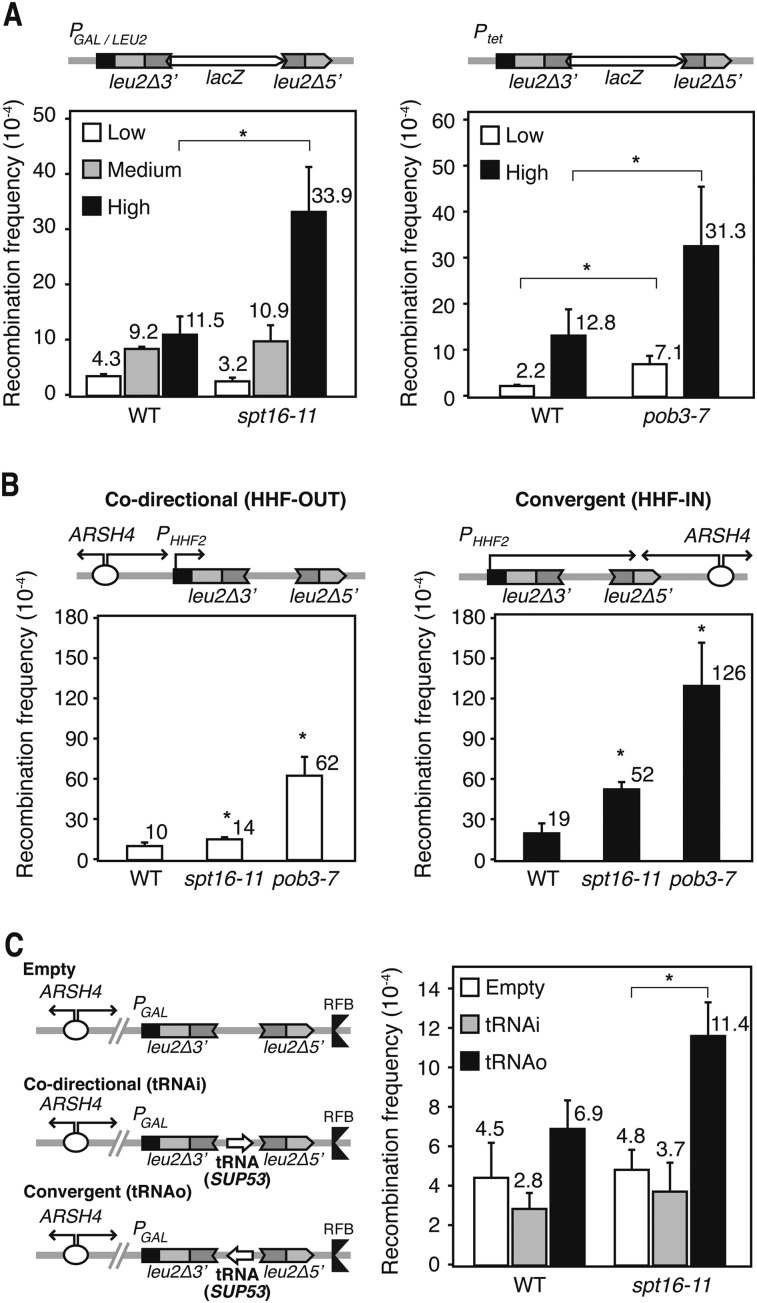
Figure 2.
Transcription-associated hyperrecombination in yFACT mutants. (A) Recombination frequency in wild-type (WT; W303-1AR5), spt16-11 (XEI-13), and pob3-7 (EIII-34) cells using the plasmid-borne direct repeat L-lacZ system expressed under the control of the GAL promoter in glucose or galactose (low and high transcription levels, respectively), the LEU2 promoter (medium), or the tet promoter with or without 5 μg/mL DOX (low and high, respectively). (*) P < 0.05 (Student's t-test). (B) Recombination frequency of the direct repeat HHF-OUT and HHF-IN systems in wild-type (W303-1ARb), spt16-11 (WXEI-48), and pob3-7 (WEIII-36) cells. Replication from the ARSH4 replication origin and transcription driven by the HHF2 promoter are in codirectional (OUT) or convergent (IN) orientations. Other details are as in A. (C) Recombination frequency of the RFB-empty, RFB-tRNAi, and RFB-tRNAo systems in wild-type (W303-1ARb) and spt16-11 (WXEI-48) cells grown in glucose. Transcription of the SUP53 tRNA gene and replication initiated at ARSH4 are either codirectional (tRNAi) or convergent (tRNAo). The RF coming from downstream from the tRNA gene is paused due to the RF barrier (RFB). (*) P < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U-test). Mean and SD of three independent experiments are depicted for each genotype.