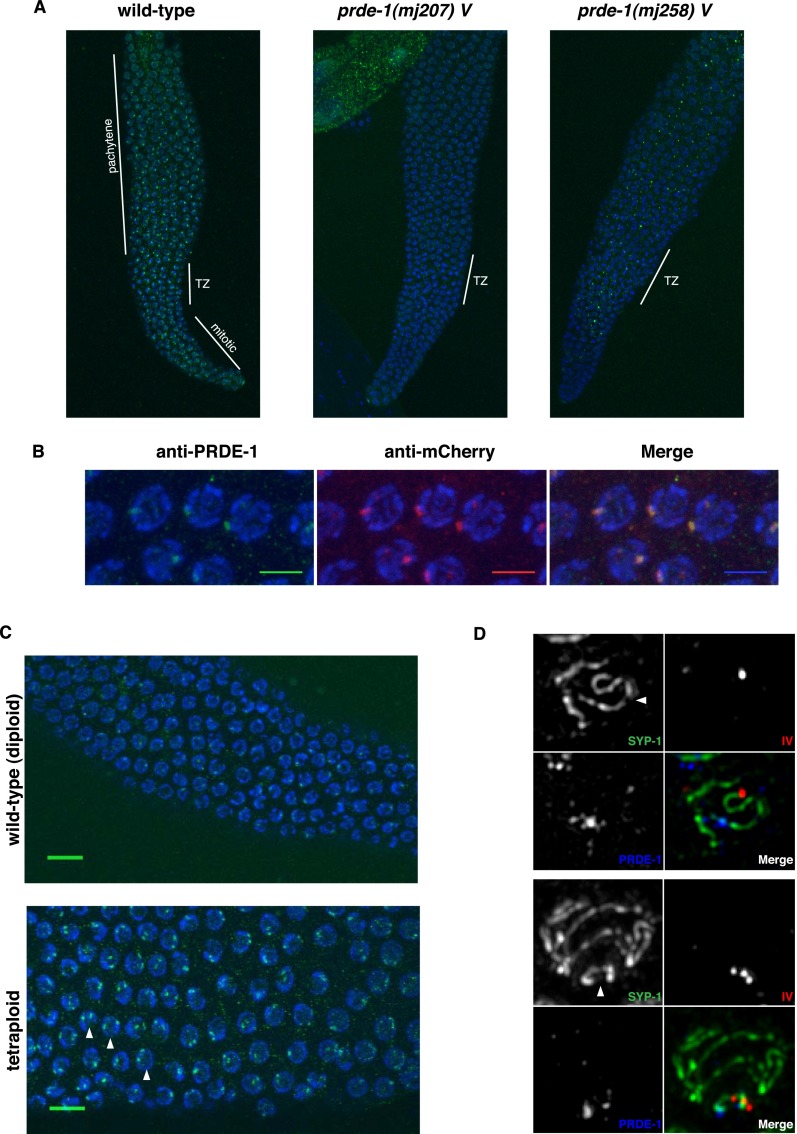
Figure 3.
PRDE-1 is a nuclear factor associated with sites of piRNA biogenesis. (A) Immunofluorescence of endogenous PRDE-1 in isolated distal gonads of C. elegans. Images are Z-projections (20× magnification; 3.0 zoom), with two putative PRDE-1-null alleles shown for comparison. Distinct regions of the C. elegans germline are marked by white lines. (TZ) Transition zone. (B) Confocal Z-projections of pachytene germ cell nuclei in an mCherry-PRDE-1-expressing strain stained for PRDE-1 and mCherry (60× magnification; 10× zoom; bars, 5 µm). (C) Immunofluorescence of endogenous PRDE-1 in pachytene nuclei of wild-type diploid (top) and tetraploid (bottom) C. elegans (confocal Z-projections at 40× magnification; 3.2 zoom). Arrowheads indicate prominent examples of nuclei with two PRDE-1 foci. Bars, 10 µm. (D) Representative deconvolved wide-field fluorescence images of pachytene nuclei stained for synaptonemal complex marker SYP-1 and PRDE-1 in combination, with DNA-FISH probe T21D12 marking the left end of chromosome IV. The top panel set shows partial projection of one nucleus, and the bottom panel set shows Z-projection of a complete nucleus. Arrowheads point to chromosome IV.