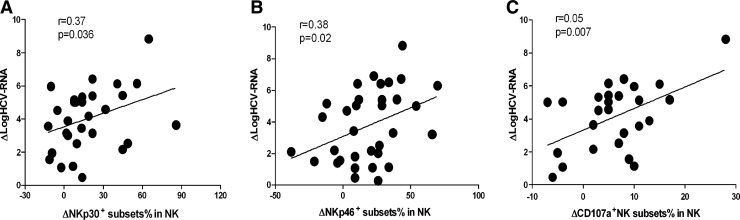
FIG. 5.
The effect of treatment with IFN on the frequency of activation receptor+ NK cells and affected functions of NK cells in CHC patients. The potential correlation of the net increases in the frequency of NKp30+ and NKp46+ NK cells with the net increases in the amount of hepatitis C virus (HCV) loads in CHC patients at 4 weeks post-treatment was analyzed. Data are expressed as mean values of individual patients at different time points post-treatment. (A) Spearman's rank correlation coefficient between the therapy-induced change in logHCV-RNA and the change in NKp30-positive NK cells was determined. Change was defined as the absolute difference between percentages at baseline and 4 weeks. ΔlogHCV-RNA=logHCV-RNAbaseline−logHCV-RNA4 week; ΔNKp30+NK cell%%=NKp30+NK cell%4 week−NKp30+NK cell%baseline. (B) Spearman's rank correlation coefficient between the therapy-induced change in logHCV-RNA and the change in NKp46-positive NK cells was determined. Change was defined as the absolute difference between percentages at baseline and 4 weeks. ΔlogHCV-RNA=logHCV-RNAbaseline−logHCV-RNA4 week; ΔNKp46+NK cell%%=NKp46+NK cell%4 week−NKp46+NK cell%baseline. (C) Spearman's rank correlation coefficient between the therapy-induced decrease in logHCV-RNA and increase in CD107a-positive NK cells was determined at 4 weeks. ΔlogHCV-RNA=logHCV-RNAbaseline−logHCV-RNA4 week; ΔCD107A+NK cell%=CD107A+NK cell%4 week−CD107A+NK cell%baseline.