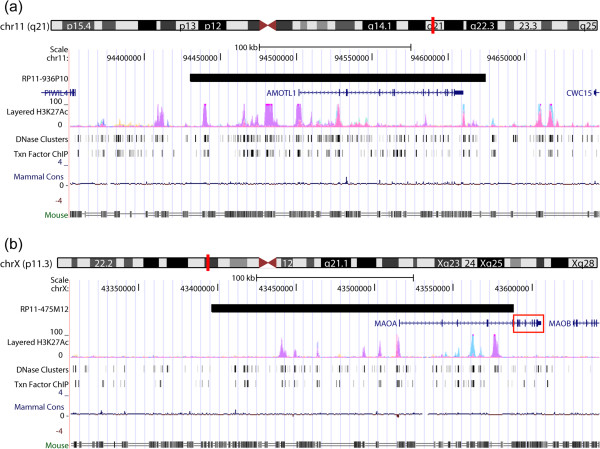
Figure 6.
Comparative genomics delineated the DNA boundaries that were sufficient for adult brain-specific expression of AMOTL1 and MAOA. Coordinates corresponding to the human bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) constructs used in this study were retrieved and visualized using the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) genome browser. (a) DNA alignment of the human AMOTL1 BAC (RP11-936P10) with the mouse genome delineated the genomic DNA boundaries sufficient for proper expression of this human gene in the anterior thalamic nuclei in both developing (P7) and adult mouse brain, regions for which this gene was chosen. (b) DNA alignment of the human MAOA BAC (RP11-475M12) with the mouse genome delineated the genomic DNA boundaries sufficient for proper expression of this human gene in the locus coeruleus (LC) in both developing (P7) and adult mouse brain, regions for which this gene was chosen. One hypothesis suggested by our results was that additional conserved regulatory elements in the 3′ coding and non-coding regions (red rectangle) could be important in narrowing the brain expression of this human gene.