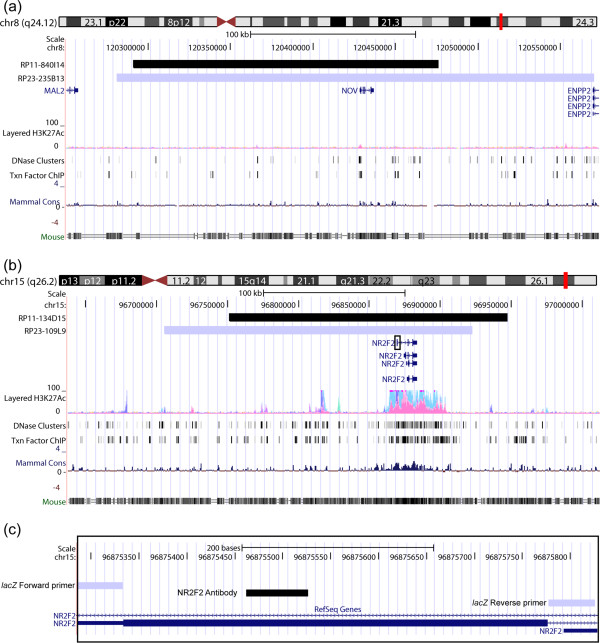
Figure 7.
Comparative genomics delineated the DNA boundaries that were sufficient for adult brain-specific expression of NOV and NR2F2. Coordinates corresponding to the human bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) constructs used in this study were retrieved and visualized using the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) genome browser. (a) DNA alignment of the human NOV BAC (RP11-840I14) (black), against both the RP23-235B13 BAC construct used in the Gene Expression Nervous System Atlas (GENSAT) mouse model (blue), and the mouse genome, delineated the genomic DNA boundaries sufficient for proper expression of this human gene in the basolateral amygdaloid nuclei, cortical layers, and pyramidal neurons in the cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) regions in the adult brain. One hypothesis suggested by our results was that additional functionally conserved regulatory elements homologous to the large non-overlapping 3′ mouse-BAC region are necessary for proper human-gene expression in the developing cortical layers at P7. (b) DNA alignment of the human NR2F2 BAC (RP11-134D15) (black), against both the RP23-109L9 BAC construct used in the GENSAT mouse model (blue) and the mouse genome, delineated the genomic DNA boundaries sufficient for region-specific expression of this human gene in the basolateral, and corticolateral amygdaloid nuclei in the adult brain. One hypothesis suggested by our results was that additional functionally-conserved regulatory elements homologous to the non-overlapping 5′ mouse-BAC region are necessary for proper expression in the developing hypothalamus at P7. Black rectangle box in (b) is shown in (c). (c) Sequence alignment using the coordinates of the primers used in the BAC lacZ retrofitting process (grey bars) and the cDNA sequence used to generate an anti-NR2F2 antibody (black bar), suggested that the absence of expression of the NR2F2-lacZ constructs in retinal amacrine cells was not attributable to detection of different isoforms of NR2F2.