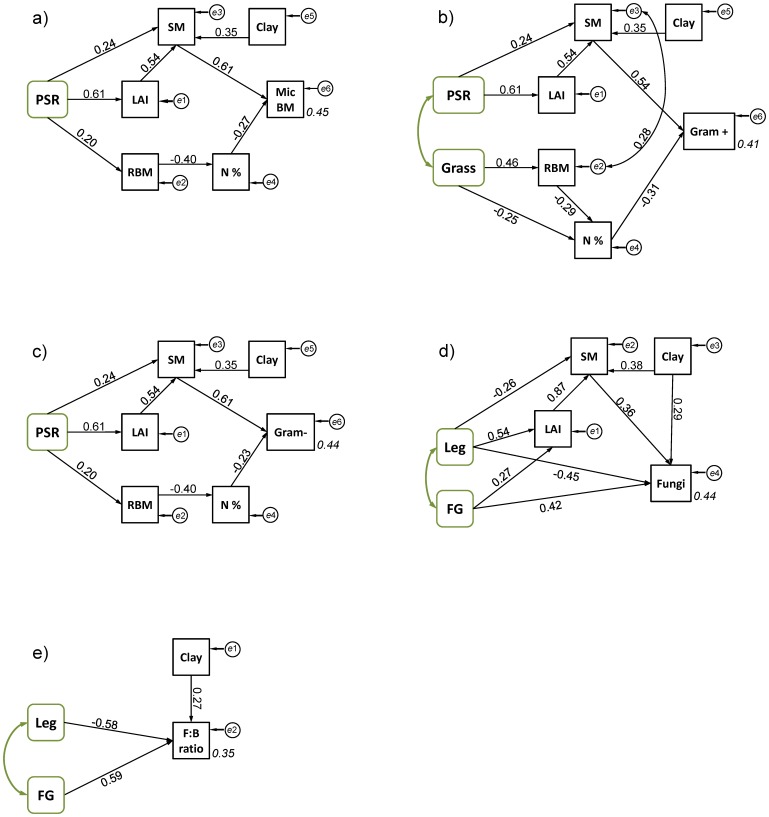
Figure 2. Minimal parsimonious models, testing direct and indirect effects of plant diversity on soil microbial community.
Minimal SEM for a) total soil microbial biomass (MicBM), b) biomass of Gram positive bacteria (Gram+), c) biomass Gram negative bacteria (Gram−), d) fungal biomass (Fungi), and e) fungal-to-bacterial biomass ratio (F:B ratio). Arrows show significant relationships between variables. Numbers next to arrows show standardized parameter estimates (i.e., standardized regression weights). Circles (e1–e6) indicate error terms, and double-headed arrows indicate significant correlations between the error terms. Squared multiple correlations (R2) for the dependent soil microbial biomass are given next to the box of the dependent variable. See the non-standardized estimates of the regression weights in Table S3a-e. Abbreviations are PSR: plant species richness, FG: plant functional group richness, LEG: presence of legumes, GRASS: presence of grasses, RBM: fine root standing biomass, N%: nitrogen concentration of fine roots, LAI: leaf area index, SM: soil moisture, Clay: clay content of soil