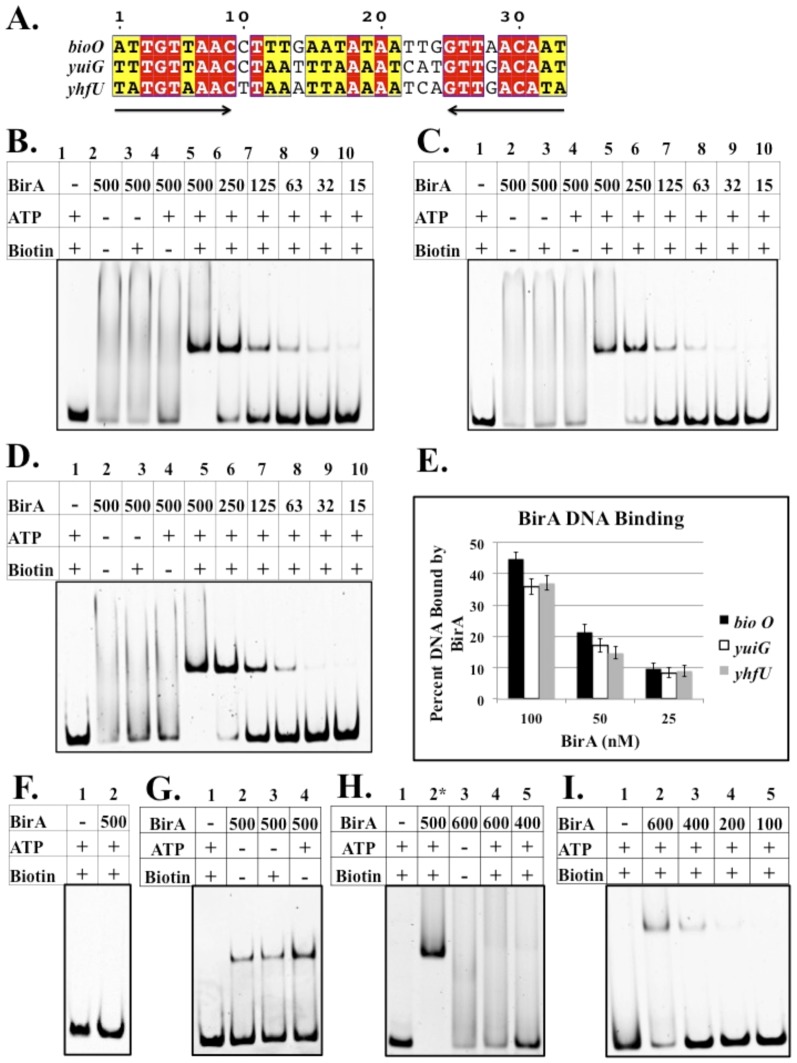
Figure 4. Sequence alignments of B. subtilis BirA DNA binding sites and electrophoretic mobility shift assay of DNA binding by BirA.
A. B. subtilis has three predicted BirA DNA binding sites: 5′ UTR of the bioWAFDBI operon, 5′ UTR of yuiG, and 5′ UTR of the yhfUTS operon. Conserved residues are highlighted in red and similar residues are highlighted in yellow. B C and D. B. subtilis BirA binding to bioO, the yuiG operator and the yhfU operator, respectively. Note that only in the presence of biotin and ATP is binding observed. E. Quantitation of DNA binding by BirA (Quantity One software). The results show the average of three independent experiments, and the error bars denote standard error of the mean. F. BirA binding to non-operator DNA (a 125 bp internal fragment of the yngHB gene that encodes BLAP). G. BirA binding to bioO without hydroxylamine treatment. Bio-5′-AMP accumulates in the active site during expression in E. coli and survives purification of BirA. H. B. subtilis BirA binding to a half site of the inverted repeat of B. subtilis bioO. Note lane 2 is positive control full-length bioO. I. B. subtilis BirA binding to E. coli bioO. A collection of all putative BirA binding sites in diverse bacteria can be found in the RegPrecise database (http://regprecise.lbl.gov/RegPrecise/).