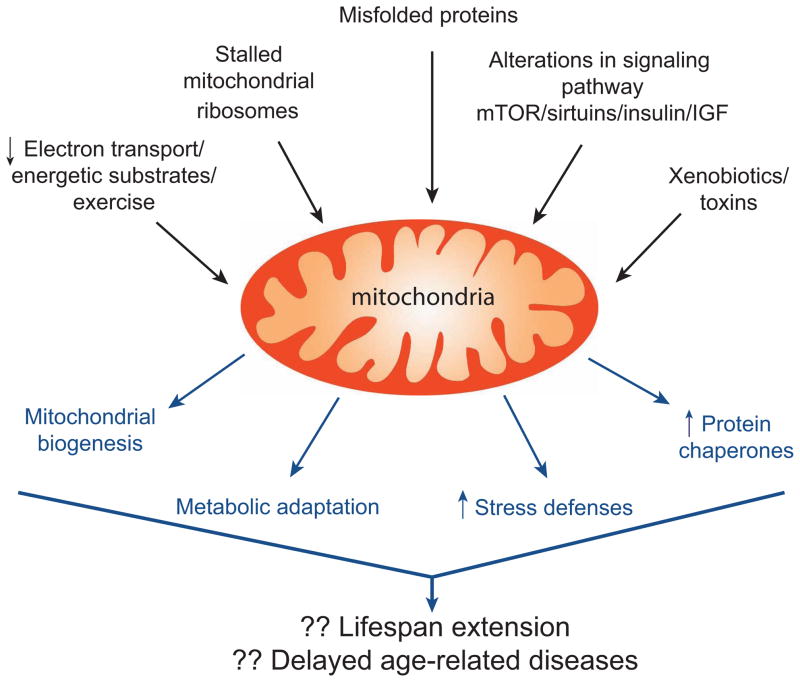
Figure 3.
The complexity of mitochondrial stresses and responses. A wide array of extrinsic and intrinsic mitochondrial perturbations can elicit cellular responses. As detailed in the text, genetic or pharmacological disruption of electron transport, incorrect folding of mitochondrial proteins, stalled mitochondrial ribosomes, alterations in signaling pathways or exposure to toxins, all appear to elicit specific cytoprotective programs within the cell. These adaptive responses include increased mitochondrial number (biogenesis), alterations in metabolism, increased antioxidant defenses and augmented protein chaperone expression. The cumulative effect of these adaptive mechanisms might be an extension of lifespan and a decreased incidence of age-related pathologies.