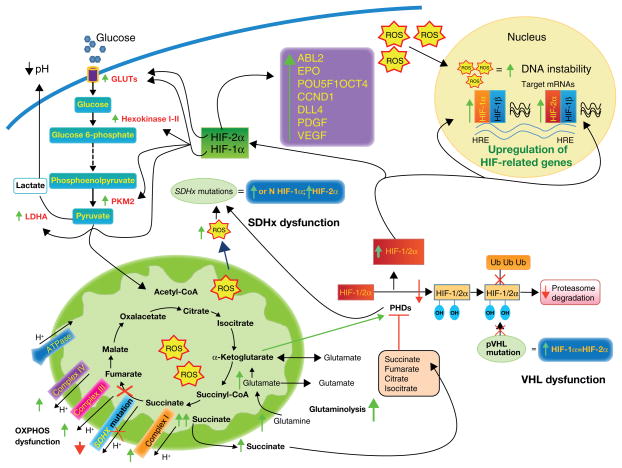
Figure 2.
Different mechanisms have been proposed to explain the link between SDHx mutations and tumorigenesis. First, the loss of function of SDH causes an accumulation of succinate and the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Second, inactivation or dysfunction of SDH inhibits the activity of HIF-α prolyl hydroxylase enzymes (PHDs). Inhibition of PHDs results in an insufficient hydroxylation of HIF-1/2α. The unhydroxylated HIF-1/2α protein cannot be degraded by the proteasome, and HIF-1/2α is stabilized. This stabilization can be overcome by α-ketoglutarate. VHL mutations result in similar inadequate HIF-1/2α proteasome degradation and HIF-1/2α stabilization. The stabilization of HIF-1α rather than HIF-2α increases glycolysis (due to overexpression of some glycolytic enzymes) and can regulate glutaminolysis. HIF-2α stabilization is involved in the direct or indirect activation of a number of genes that are known to be involved in the inhibition of apoptosis, tumorigenesis, and angiogenesis. The stabilization of HIF-1/2α leads to an upregulation of HIF-related genes due to binding to hypoxia-responsive elements (HRE) and to an overexpression of hypoxia-related genes. Increased ROS accumulation results in oxidative DNA damage and genomic instability and inhibits PHDs, similarly to the accumulation of succinate. Increasing activity of complex I, III, and IV may be a compensatory reaction to a lack of or decreased complex II activity in SDHx- related tumors.
Abbreviations: ABL2- ABL2 protein tyrosine-protein dinase; CCDN1- cyclin D1; DLL4- delta-like protein 4; EPO- erythropoietin; GLUTs- glucose transporters; HIF- hypoxia-inducible factor; HRE- hypoxia-responsive elements; LDH-A- lactate dehydrogenase A; OXPHOS- oxidative phosphorylation; PDGF- platelet-derived growth factor; PHDs- prolyl hydroxylases; PKM2- pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme 2; POU5F1 OCT4- POU domain, class 5, tarnscription factor 1 isoform; pVHL- protein of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene; ROS- reactive oxygen species; SDH- succinate dehydrogenase; Ub- ubiquitin; VEGF- vascular endothelial growth factor.