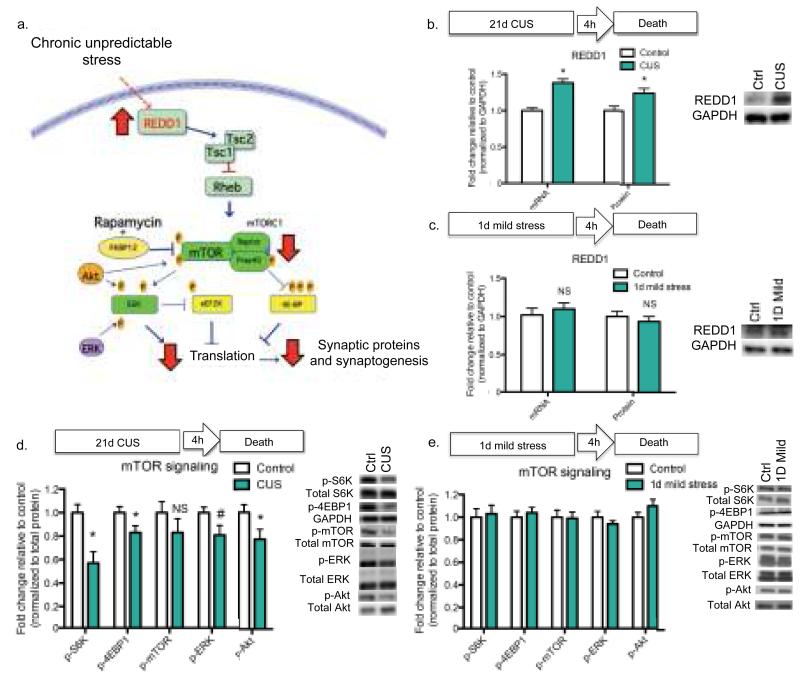
Figure 1. Chronic unpredictable stress increases REDD1 and decreases mTORC1 signaling in rat PFC.
(a) Schematic showing how increased REDD1 could result in decreased mTORC1 signaling via Rheb and the TSC1/TSC2 complex (10), and subsequent decreased translation and synaptogenesis. (b) Rats received 21 d of CUS or regular handling (control) then sacrificed 4 h following the final stressor. Results are mean ± SEM fold change of PFC REDD1 mRNA [CUS n=8; Control n=8] and protein [CUS n=10; Control n=12] relative to control. (c) Rats received 1 d of mild stress or handling (control) then sacrificed 4 h following the final stressor. Results are mean ± SEM fold change PFC REDD1 mRNA [1 d mild stress n=6; control n=6] and protein [1 d mild stress n=6; control n=6] relative to control. For (b) and (c), protein levels were normalized to GAPDH, and representative blots are displayed to the right. (d) Rats received 21 d of CUS (n=10) or regular handling (control) (n=12), then sacrificed 4 h following the final stressor. (e) Rats received 1 d mild stress (n=6) or handling (control) (n=6), then sacrificed 4 h following the final stressor. For (d) and (e), phospho-protein levels in PFC were normalized to total protein levels; results are shown as mean (± SEM) fold change. Representative blots are displayed to the right. (*) p < 0.05 (#) p < 0.10 relative to control. Abbreviations: mTORC1, mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Akt, serine threonine kinase or protein kinase B; S6K, P70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase; 4E-BP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1; TSC, tuberous sclerosis complex.