Figure 1.
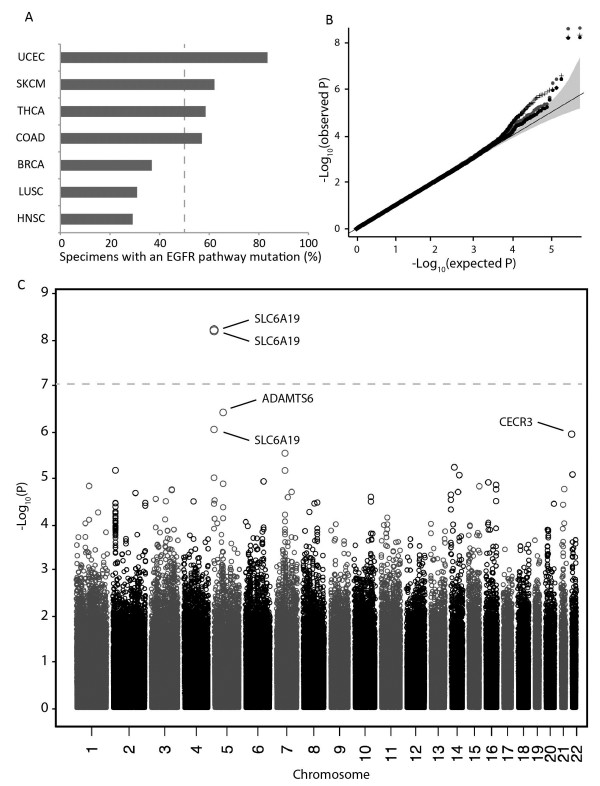
Frequencies of somatic mutation in the EGFR pathway for different solid tumour types. (A) TCGA tumour specimens were classified by mutation status for commonly mutated components of the EGFR pathway, including EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA and PTEN. The EGFR pathway was considered mutant if a non-synonymous mutation was detected in one or more of these factors. High and low mutation frequencies were determined by a 50% cutoff (dashed line). Cancer types with little or no evidence of EGFR pathway mutation are not shown. Somatic mutations for individual specimens were obtained from publicly available TCGA somatic mutation data (based on MutSig analysis of whole-exome sequencing). LUAD was excluded from the study due to reported strong environmental association between KRAS mutation status and smoke exposure [17]. (B) Quantile-quantile plot of GWAS SNP p-values for association with somatic mutation status of the EGFR pathway. Cancer types included in the analysis were: UCEC, SKCM, THCA and COAD. Black points show p-values adjusted for population stratification using genomic inflation control; crosses show p-values adjusted for population stratification by incorporation of the top 10 eigenvectors as covariates; grey points show non-adjusted p-values. (C) Manhattan plot of GWAS SNP p-values for association with somatic mutation status of the EGFR pathway. P-values were adjusted for genomic inflation. Grey dashed line indicates the genome-wide significance threshold (p = 8.78 × 10-8). Abbreviations: UCEC – uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma. SKCM – skin cutaneous melanoma. THCA – thyroid carcinoma. COAD – colorectal adenocarcinoma. BRCA - breast invasive carcinoma. LUSC - lung squamous cell carcinoma. HNSC – head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. LUAD – lung adenocarcinoma.
