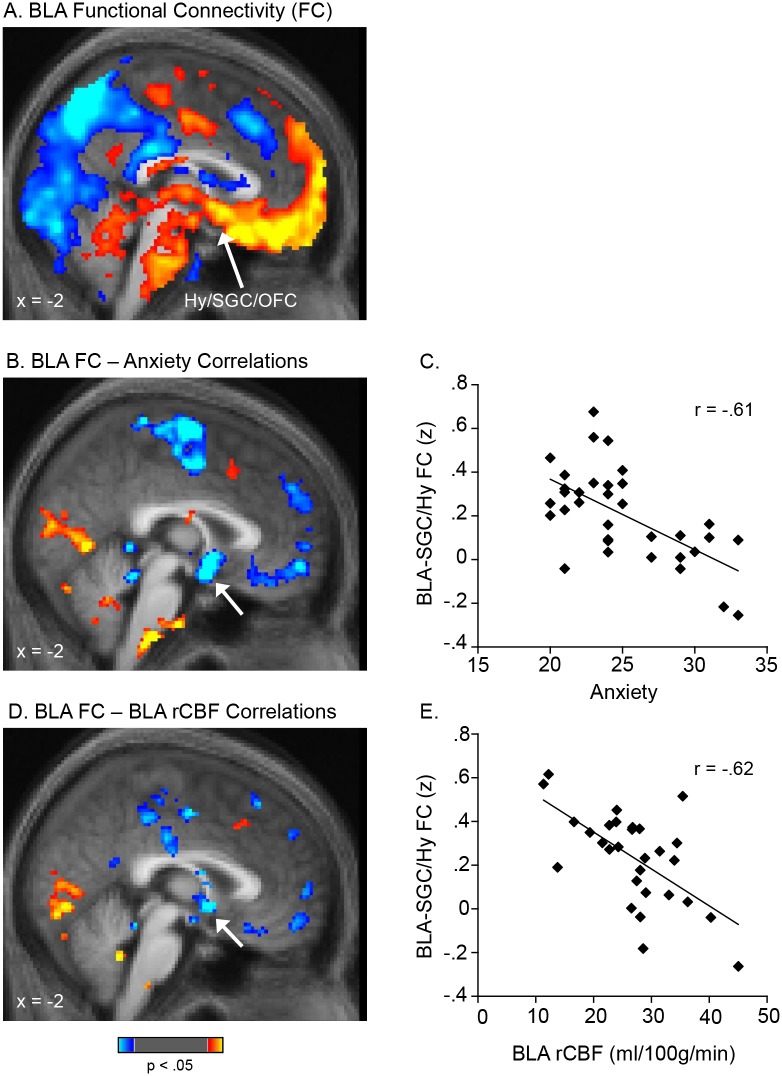
Figure 3. Functional connectivity between the BLA and mPFC is inversely correlated with BLA perfusion and anxiety levels.
An average map of basolateral amygdala (BLA) functional connectivity is shown in A. A whole-brain voxel-wise regression revealed that the strength of connectivity between the BLA and mPFC was negatively correlated with both: anxiety levels (B, C) and BLA perfusion (D, E). In A, B, and D, voxels with positive connectivity with the BLA (A) or showing positive correlations between their connectivity with the BLA and anxiety levels (B) or BLA perfusion (D) are shown in warm colors; voxels with negative correlations are shown in cool colors. The scatter plots in C and E are derived from the accompanying voxel-wise regression maps shown in B and D and are presented for the purpose of illustrating the range of values only. Data are displayed at a threshold of p<.05. The clusters indicated with arrows in B and D met a cluster-wise correction (FWE, p<.05) within the ventral mPFC. The peaks of the clusters in B (4, 2, −7) and D (2, 4, −4) were localized to the posterior-most portion of the SGC (with both clusters extending into the hypothalamus) using two independent atlases (the Talairach and Tournoux Stereotaxic Atlas [46] and the Wake Forrest University (WFU) PickAtlas [47]; see Methods). Prior work further supports this localization; previously reported sites that have been localized to the SGC (BA25), as well as an architectonic mapping of BA25 [68], overlap with the two clusters reported here, with nearby peaks: 4, 2, −4 [69]; −2, 6, −6 [8]; −2, 8, −10 [70]; −3, 9, −6 [71]; −4, 9, −12 & 2, 11, −7 [72]; 0, 8, −16 [73]. BLA, basolateral amygdala; FC, functional connectivity; Hy, hypothalamus; SGC, subgenual cingulate gyrus; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex.