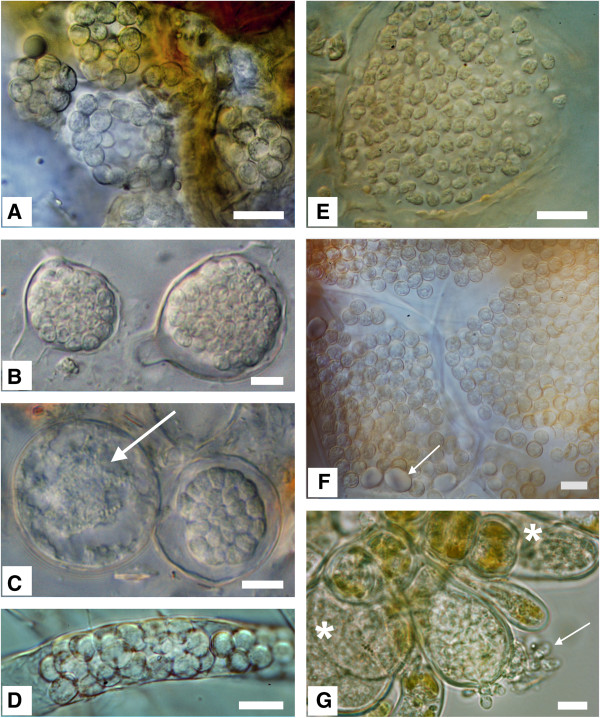
Figure 2.
Morphology of resting spores from selected phytomyxids. Bar?=?10 μm: left column: Plasmodiophorida, right column: Phagomyxida. Left top to bottom: 2A: Sorosphaerula viticola: hollow sporosori in the roots of Vitis sp. 2B: Woronina pythii: resting spores in Pythium sp. 2C: W. pythii in Pythium sp.: lobose plasmodium, just starting to develop into resting spores (arrow); right more or less mature resting spores. 2D: Ligniera junci: resting spores in the root hairs of Juncus effusus. Right top to bottom: 2E: Maullinia sp. resting spores in Durvillea antarctica. The resting spores are slightly irregular in size and shape. 2F: Plasmodiophora diplantherae: Resting spores in Halodule sp. Resting spores are in enlarged cells of the host, Arrow: starch grains. 2G: Maullinia ectocarpii: hatching zoospores (arrow) from an enlarged infected cell of the host Ectocarpus fasciculatus. Asterisk: plasmodia in enlarged host cells.