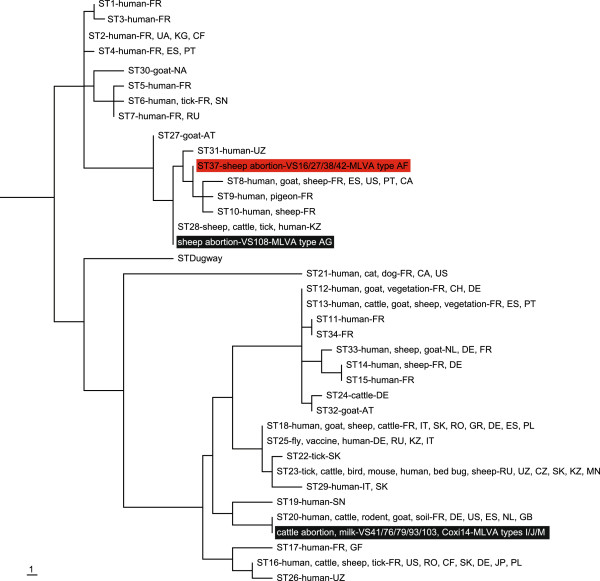
Figure 2.
Parsimony tree showing the placement and phylogenetic relationships of the sequence types (ST) from this study with known STs [19], rooted according to Pearson et al. [33]. Highlights indicate the placement of the STs of our samples; the red highlight denotes the newly proposed ST37. One hundred and twelve polymorphisms from Hornstra et al. [26] were used to construct this phylogeny and resulted in 156 equally parsimonious trees, the first of which is depicted above. Tree length is 120 and the homoplasy index (excluding uninformative characters) is 0.0769. Isolate origins and sources are given according to previous publications [19,20,25,26,28,29,35-38] using the following location codes: Austria (AT), Canada (CA), Central African Republic (CF), Czech Republic (CZ), France (FR), French Guiana (GF), Germany (DE), Greece (GR), Italy (IT), Japan (JP), Kazakhstan (KZ), Kyrgyzstan (KG), Mongolia (MN), Namibia (NA), Netherlands (NL), Poland (PL), Portugal (PT), Romania (RO), Russian Federation (RU), Senegal (SN), Slovakia (SK), Spain (ES), Switzerland (CH), Ukraine (UA), United Kingdom (GB), United States (US) and Uzbekistan (UZ).