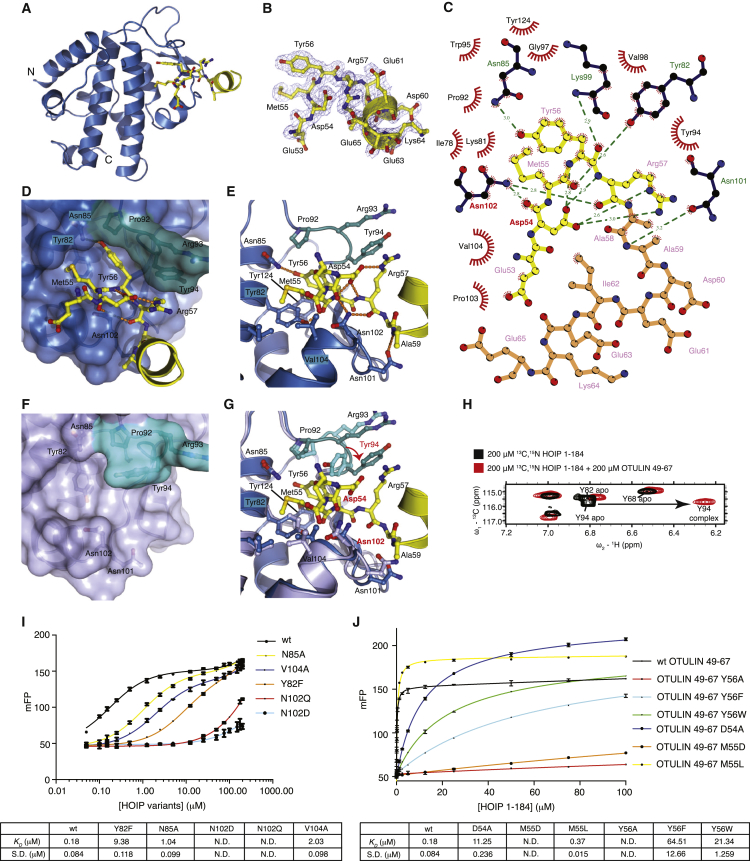
Figure 3.
Structure of HOIP Bound to OTULIN Peptide
(A) Structure of HOIP PUB domain (aa 5–180; blue) bound to the OTULIN PIM peptide (yellow). The peptide is in ball-and-stick representation with blue nitrogen and red oxygen atoms.
(B) A weighted 2|Fo|-|Fc| map contoured at 1 σ covering the OTULIN PIM peptide colored as in (A).
(C) LIGPLOT representation of the HOIP-OTULIN interaction. Residues in the PIM (aa 53–57) are shown in yellow, and the C-terminal extension of the PIM is shown in orange. Hydrogen bonds are shown by green dashes, and van der Waals contacts are shown as red fans.
(D) PIM pocket shown in surface representation in the HOIP-OTULIN complex colored as in (A). Residues 92–94, including the mobile Tyr94, are colored green.
(E) Close-up view of the OTULIN PIM peptide in the HOIP PIM pocket, colored as in (A), showing hydrogen bonds as orange dotted lines.
(F) PIM pocket shown in surface representation in apo HOIP, in which Tyr94 (green) partly occludes the PIM pocket.
(G) Superposition of apo and PIM-peptide-bound HOIP highlighting the conformational change in Tyr94 side chain.
(H) A conformational change of the Tyr94 side chain is resolved in the aromatic region of 13C-HSQC spectra, with HOIP alone (black) and the HOIP OTULIN PIM complex spectrum shown in red. The shifting resonance indicated by an arrow corresponds to the Cε of Tyr94. Only the Cε region of the aromatic 13C-HSQC is shown.
(I) Fluorescent polarization assay of wild-type OTULIN PIM peptide binding to purified HOIP (aa 1–184) PIM pocket mutants. Binding parameters are listed below. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and errors represent SD from the mean.
(J) Binding of HOIP PUB domain (aa 1–184) to OTULIN peptides (aa 49–67) with the indicated point mutations in the PIM performed as in (I). Binding parameters are listed below.