Figure 1.
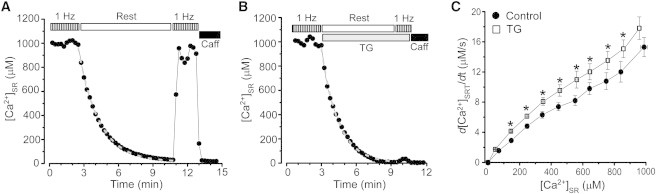
Effect of SERCA inhibition on rest-dependent [Ca2+]SR decline. The decline of [Ca2+]SR during rest in control conditions (A) and after SERCA inhibition with TG (10 μM; B). Before rest, myocytes were electrically stimulated at the constant rate of 1 Hz. Application of 10 mM caffeine at the end of the experiment caused complete depletion of [Ca2+]SR. During the period of rest, the experimental points were fitted with a single exponential function (dashed gray lines). (C) The rate of [Ca2+]SR decline during rest as a function of diastolic [Ca2+]SR measured in control conditions (●) and after SERCA inhibition (□). ∗P < 0.05 vs. control.
