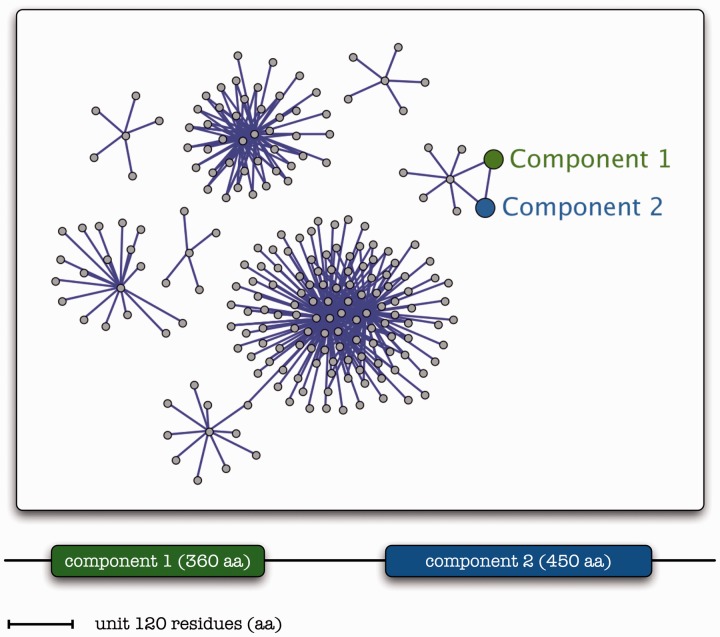
Figure 1.
A pictorial representation of the gene fusion detection/association inference process. A composite protein (bottom) with two domains exhibits sequence similarities to two component homologs [Component 1 (green) and Component 2 (blue) with 360 and 450 amino acid residues (aa), respectively—not shown]. The total length of the fictitious protein sequence is 1200 residues, drawn to scale—unit shown (120 residues). Networks of associations, with nodes (grey) corresponding to genes/proteins and links (purple) depicting pairwise interactions, can thus include the corresponding (color-coded) component proteins identified by their similarity to composite proteins and inferred to be functionally linked.