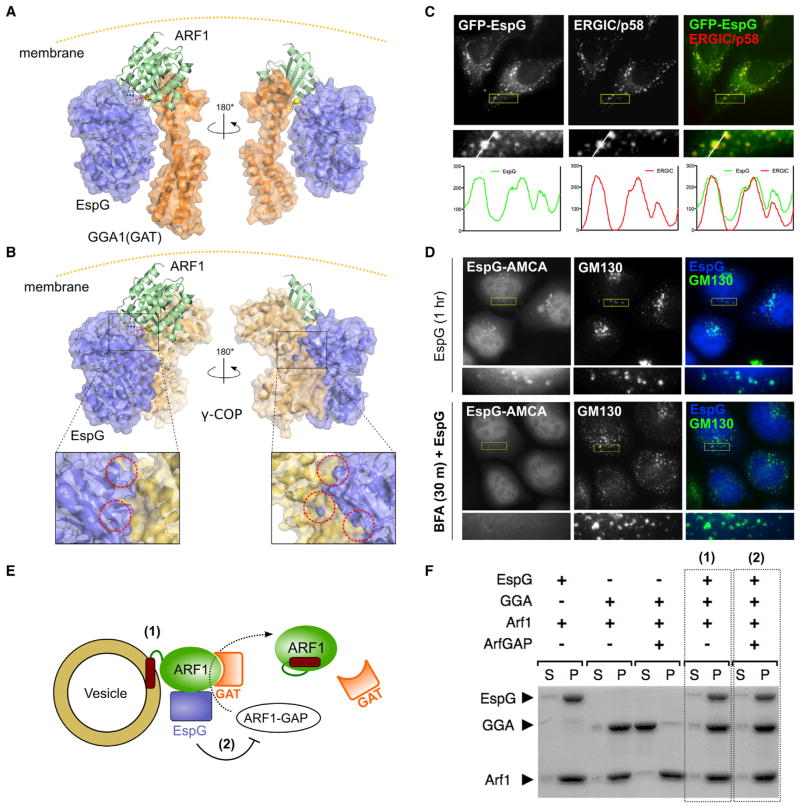
Figure 5. EspG Functions Selectively through Downstream Interactions of Active ARF1.
(A) Structural model of EspG bound to the ARF1/GGA1(GAT) complex, based on EspG/ARF1 (1PCR) and ARF1/GGA1(GAT) (1J2J and1O3X) X-ray structures.
(B) Structural model of EspG bound to the ARF1/γ-COP complex, based on EspG/ARF1 (1PCR) and EspG/γ, ζ-COP (3TJZ) structures. Insets show major steric clashes, highlighted with dotted circles.
(C) Fluorescence micrographs show localization of GFP-EspG to p58-positive ERGIC membranes.
(D) The membrane association of EspG is dependent on membrane-bound ARF1. Fluorescently labeled EspG is localized to fragmented endomembranes during microinjection, but is cytosolic when cells are pretreated with BFA.
(E) Experimental setup to examine (1) membrane recruitment of downstream effectors by ARF1 and (2) the susceptibility of the ARF1/effector complex to GAP-mediated inactivation in the presence of EspG.
(F) Liposome pull-down experiments for the setup described in (D). EspG allows recruitment of the ARF1 effector to membranes (1) and prevents its release due to ARF1 inactivation by ArfGAP (2).
See also Figure S4.