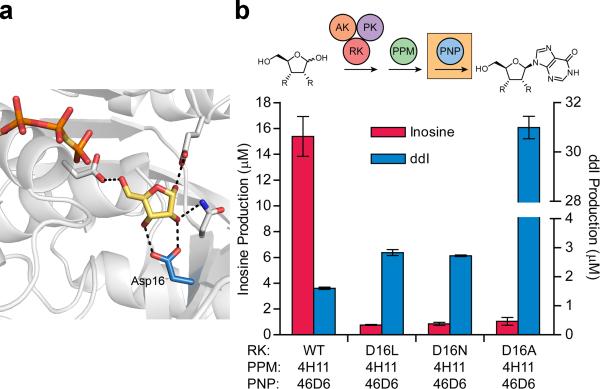
Figure 4. Optimization of RK via didanosine production assay.
(a) The interaction between the active site residue Asp16 and bound ribose is highlighted in wild-type E. coli RK (PDB entry 1GQT28). This interaction was targeted for removal in preliminary site directed mutagenesis studies by mutation to leucine, asparagine and alanine (water molecules not shown). (b) RK variants were tested for production of inosine and didanosine from ribose and dideoxyribose, respectively, using the three enzyme engineered pathway and ATP regeneration cycle. Data are mean ± s.d. (n=2).