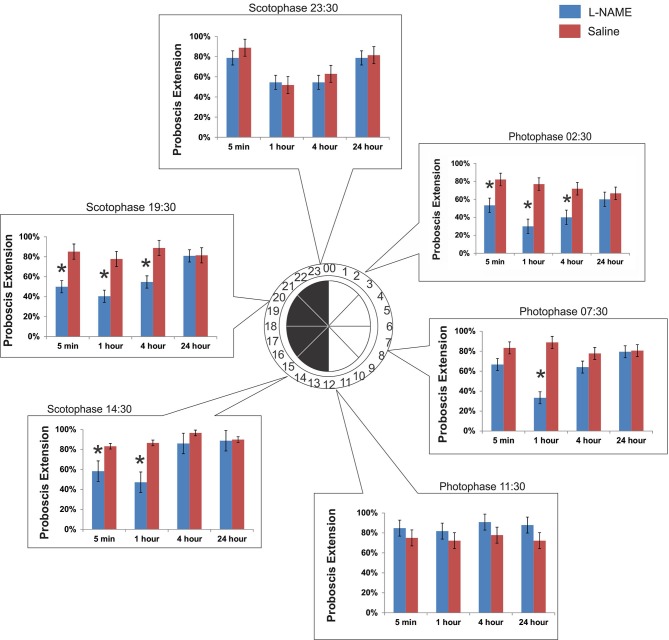
Figure 2.
The time of conditioning changes the effect of NO in memory. Six separate experiments were performed to test the role of diurnal time in olfactory learning and memory and the role of NO. Six time points were chosen: 3 in photophase and 3 in scotophase. Conditioning began at the start of the time point (e.g., 14:30). After conditioning, animals were tested for their response to the CS (hibiscus odor) by observing the PER at 5 min, 1 h, 4 h, and 24 h. Asterisks denote significance between treatment groups (saline-injected and L-NAME injected) using a one-way ANOVA test. Total N = 136.