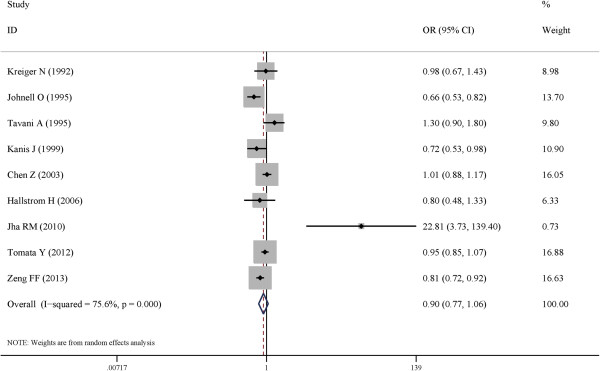
Figure 2.
Forest plot of risk estimates of the association between tea drinking and risk of fracture. In a random-effects meta-analysis, tea intake was not associated the incidence of fracture (OR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.78-1.04). A significant heterogeneity was observed when all the 9 studies were pooled (I2, 73.6%; P < 0.001).