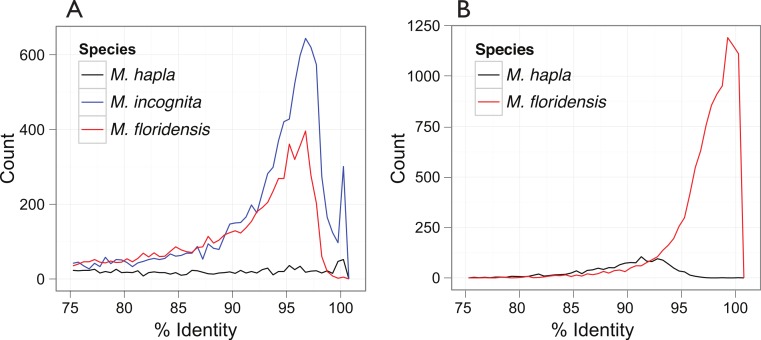
Figure 3. Inter- and intra-genomic identification of duplicated protein-coding regions.
(A) Each coding sequence from each of the three target genomes (M. hapla, M. incognita and M. floridensis) was compared to the set of genes from the same species. The percent identity of the best matching (non-self) coding sequence was calculated, and is plotted as a frequency histogram. Both M. incognita and M. floridensis show evidence of the presence of many duplicates, while M. hapla does not. (B) The M. incognita gene predictions were compared to the M. floridensis genome and the M. hapla gene set. For each M. incognita gene, the similarity of the top matches in each genome was assessed. M. incognita has many genes that are highly similar to those of M. floridensis (similarity >98%). This contrasts with the matches to M. hapla, where the modal similarity is ∼92%, and there is no peak of high-similarity matches.