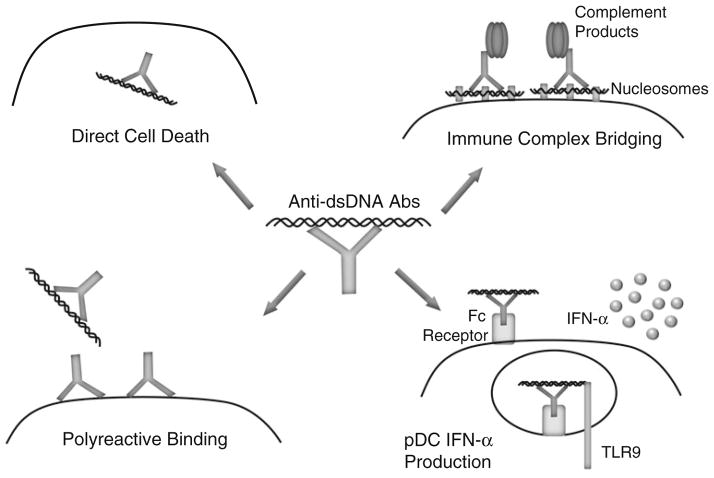
Fig. 1.
Pathogenic mechanisms of anti-dsDNA antibodies. Anti-dsDNA antibodies can cause pathology by a variety of non-exclusive mechanisms: directly enter cells and induce apoptosis by binding cellular DNA (top left); bind cell surface, non-dsDNA antigens in a polyreactive manner (bottom left); bind to the DNA component of nucleosomes that electrostatically bridge the immune complex to the cell surface (top right); and induce IFN-α secretion after Fc-mediated uptake by delivering dsDNA ligand to TLR9 (bottom right)