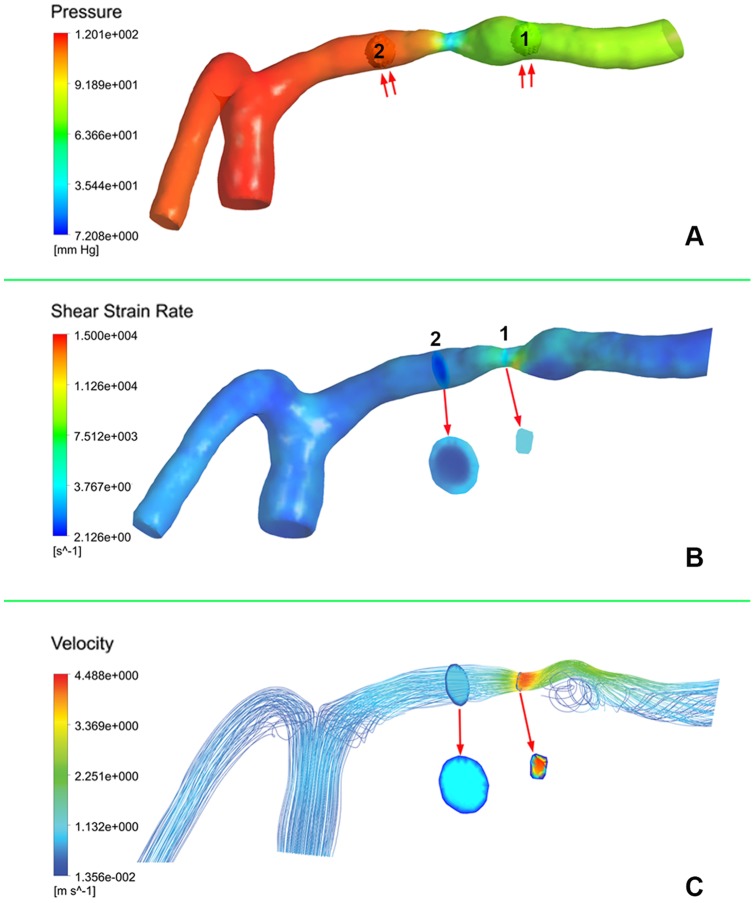
Figure 1. Evaluation of computational fluid dynamics model of an atherosclerotic lesion of left middle cerebral artery.
A: Post- and pre-stenotic pressures were measured using spherical volumes-of-interest (VOI, double arrows) at the first anatomically normal diameters distal (VOI 1) and proximal (VOI 2) to the lesion, respectively. The pressure ratio was calculated by dividing the mean pressure at VOI 1 by the mean pressure at VOI 2. B: Shear strain rates (SSR) were respectively measured at the stenotic throat (cut-plane 1) and at the first anatomically normal diameter (cut-plane 2) proximal to the lesion, by using cut-planes perpendicular to the direction of blood flow (arrow). The SSR ratio was calculated by dividing the SSR averaged over cut-plane 1 by the SSR averaged over cut-plane 2. C: Velocities were similarly measured (arrow) as with the SSRs, and the velocity ratio was similarly calculated as with the SSR ratio.