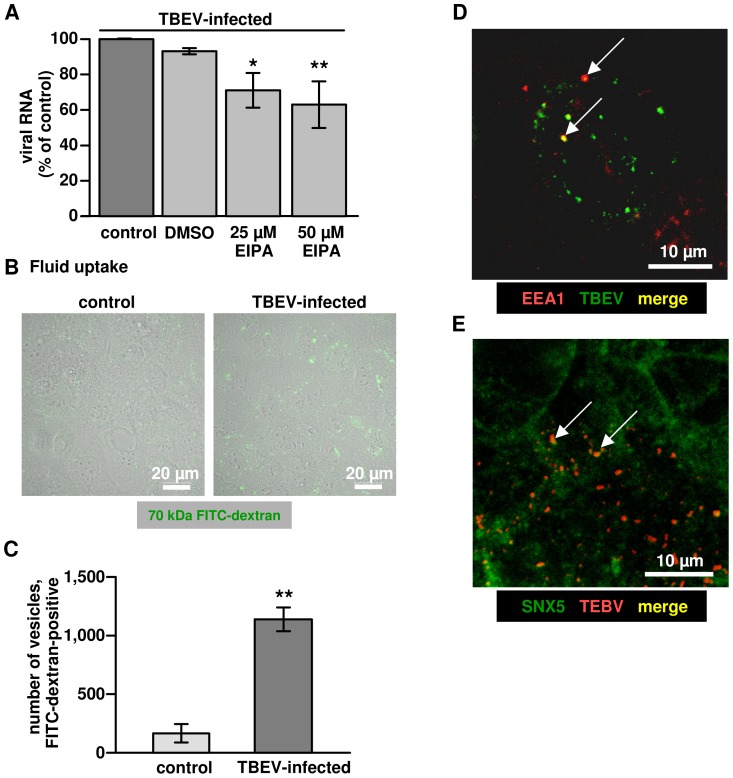
Figure 5. Characteristics of macropinocytosis in TBEV infected Caco-2 cells.
(A) Impaired TBEV entry by EIPA. Dose-dependence of EIPA-induced inhibition of TBEV entry. Caco-2 cells were pre-treated with EIPA for 30 min, followed by incubation with TBEV in the presence of the inhibitor. After 1 h, virus entry was monitored by RT-qPCR. n = 4; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 to DMSO control in Student's t test. (B) Fluid uptake. Accumulation of intracellular FITC-dextran (green) induced by TBEV infection. Caco-2 cells were treated with TBEV strain K23 for 1 h and then washed with PBS. Subsequently, cells were incubated with FITC-labeled dextran (1 mg/ml). After 4 h, cells were washed, fixed and observed by confocal microscopy. One representative image of a triplicate is depicted. (C) Accumulation of dextran in cells was analyzed by counting the total number of intracellular FITC-dextran-containing vesicles in a low power field using ImageJ. **P<0.01 (n = 3). (D) Immunofluorescence microscopy. TBEV co-localization (as merge in yellow, indicated by arrows) with early endosomal antigen-1 (EEA1) or (E) Sorting nexin-5 (SNX5) after virus entry. Cells were fixed and stained for TBEV anti-E protein and EEA1 or SNX5 with primary antibodies, followed by secondary antibodies as indicated in the image. A representative image (63× objective) is shown. Yellow dots as merge indicate TBEV particles in co-localization with EEA1 or SNX5.