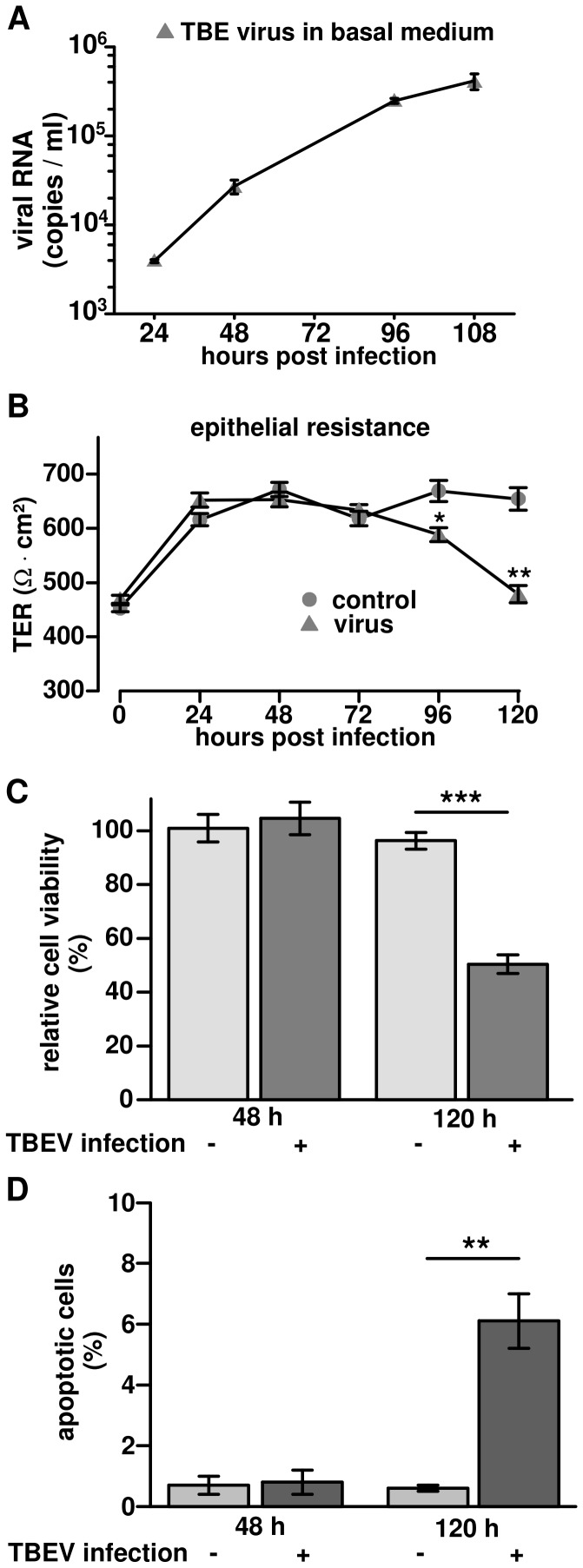
Figure 6. Translocation of TBEV through Caco-2 monolayers without affecting transepithelial electrical resistance (TER).
(A) Virus amount in basal medium. Polarized Caco-2 monolayers grown on permeable supports were infected with TBEV strain K23 from the apical surface. Basal medium was harvest at different time points and viral RNA in each sample was detected by RT-qPCR. The data were displayed as mean with standard deviation. (B) Transepithelial electric resistance (TER) measurements during TBEV infection. Polarized Caco-2 monolayers, grown on permeable supports, infected with TBEV K23 (circles) from the apical surface. Non-infected cells served as controls (triangles). TER values were measured from 0 h to 120 h post infection. n = 5, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 to control in Student's t test. (C) Cell viability during TBEV infection. Caco-2 cells were infected with TBEV strain K23 at an MOI of 1 and cell viability was analyzed by MTT assay. Cell viability was measured and calculated as a percentage of non-infected control cells. Data were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. (D) Analysis of TUNEL-positive cells. Confluent Caco-2 cells were infected with TBEV strain K23 and apoptosis was detected by a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling (TUNEL) at 48 h and 120 h post infection. The ratios of TUNEL-positive cells to all cells were analyzed in 4 low-power fields from 3 independent samples of each group. **P<0.01.