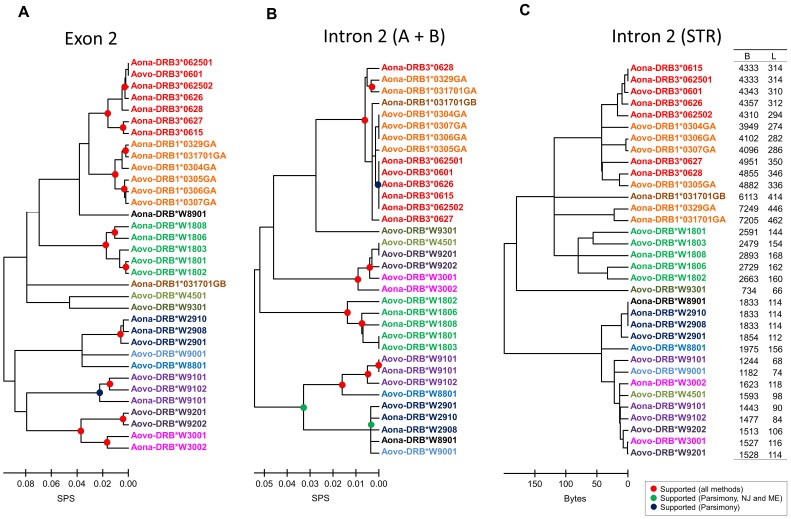
Figure 4. Comparison amongst exon 2, alignable sectors of intron 2 and intron 2 STR. A. Maximum likelihood tree constructed from Aotus MHC-DRB exon 2 sequences (34 OTUs, 344 aligned positions).
The analysis used the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model with invariable positions and Gamma distribution (5 categories, +G, parameter = 0.2659, +I, 51.7393% sites). B. Maximum likelihood tree constructed from Aotus MHC-DRB intron 2 (A+B) sequences (34 OTUs, 271 aligned positions). The analysis involved using the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model with invariable positions and Gamma distribution (5 categories, +G, parameter = 0.2378, +I, 0.0% sites). C. Complete linkage tree constructed from Aotus MHC-DRB intron 2 STR sequences. The analysis was done using a Manhattan distance over Lempel-Ziv compression. Compression in bytes (B) and length in nucleotides (L) are also shown. Nodes indicated by red dots were supported by all methods. Nodes shown by green dots were supported by parsimony (>70% bootstrap), Neighbour joining and minimum evolution tests (>70% bootstrap and >95% interior branch test), but not in maximum likelihood analysis. Nodes represented by blue dots were supported only by parsimony (bootstrap >70%), but not in maximum likelihood analysis. Bootstrap and interior branch tests were performed using 1,000 replicates. The scale bar represents substitutions per site (A and B), and bytes (C). Abbreviations and GenBank accession numbers of the analysed sequences are shown in Table S1 (within File S1).